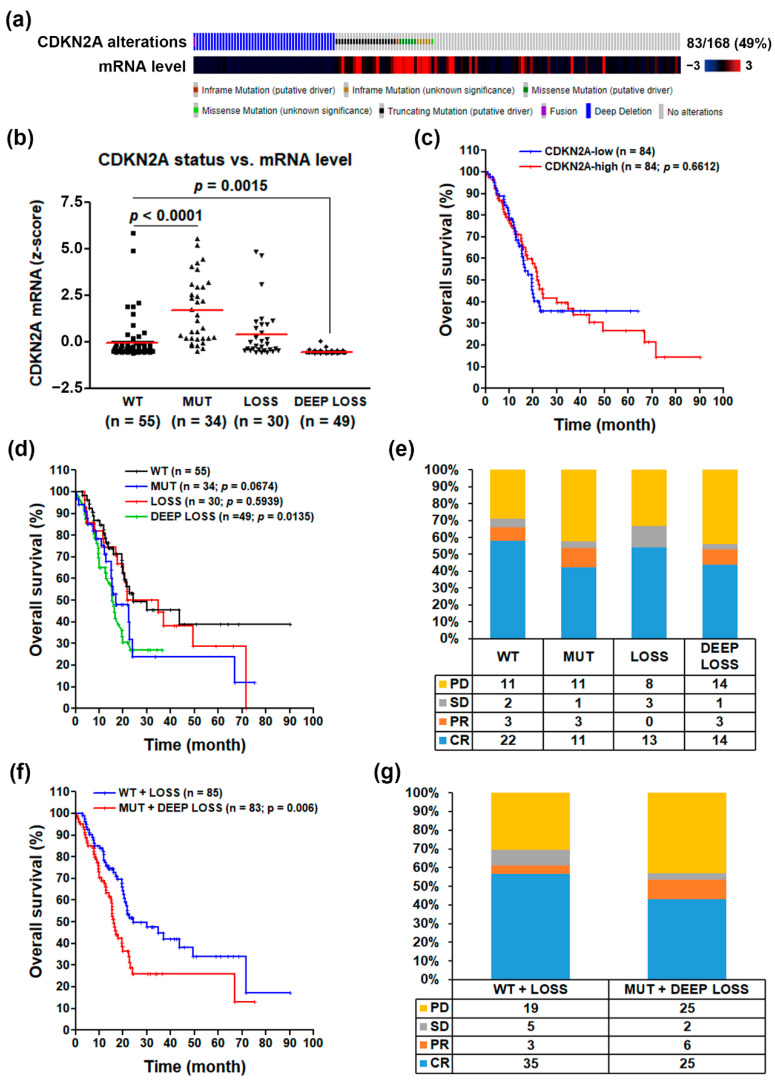
Figure 1.
The clinical impact for the loss of cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A) functional activity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. (a) The genetic alterations and mRNA expression levels of CDKN2A gene in 168 pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients; (b) the correlation between CDKN2A genetic alterations (WT for wildtype; MUT for mutation; LOSS for shallow deletion; and DEEP LOSS for deep deletion) and CDKN2A mRNA expression levels; (c) the correlation between CDKN2A mRNA levels and PDAC patients’ overall survivals; (d) the correlation between CDKN2A genetic alterations (WT; MUT; LOSS; and DEEP LOSS) and PDAC patients’ overall survivals; (e) the correlation between CDKN2A genetic alterations and PDAC patients’ primary therapy outcomes (PD for progressive disease; SD for stable disease; PR for partial remission/response; and CR for complete remission/response); (f) the correlation between CDKN2A genetic alterations (MUT + DEEP LOSS vs. WT + LOSS) and PDAC patients’ overall survivals; (g) the correlation between CDKN2A genetic alterations (MUT + DEEP LOSS vs. WT + LOSS) and PDAC patients’ primary therapy outcomes.