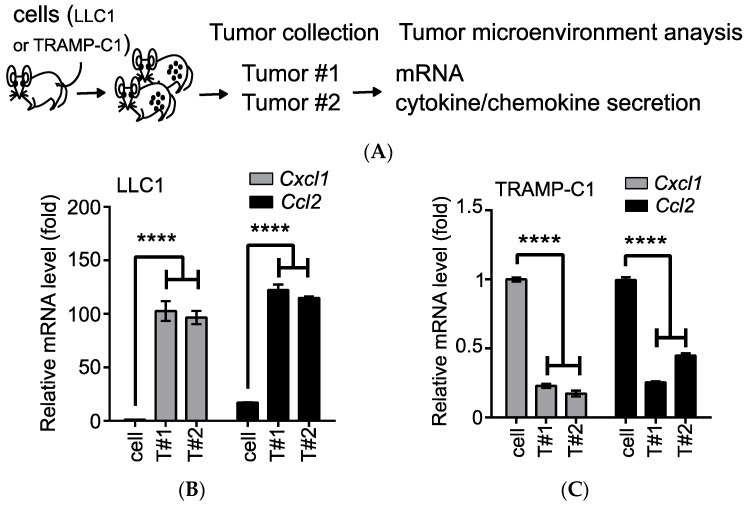
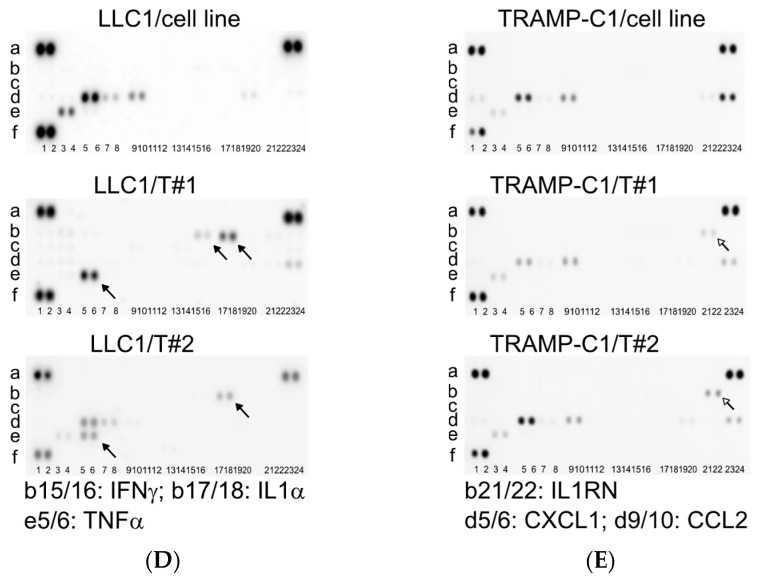
Figure 1.
Transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP)-C1-derived tumors show tumor-type-specific anti-inflammatory environments. (A) The outline of analyzing the tumor microenvironment. Following a subcutaneous injection, tumor tissues (Tumor#1 (T#1) and T#2) were analyzed for transcription expressions of selected genes (mRNA) or processed to single-cell suspensions without red blood cells to detect the secreted factors in the conditioned medium (cytokine/chemokine secretions). (B) Comparison of mRNA levels of proinflammatory chemokines (Cxcl1 and Ccl2) between the LLC1 cell line and its derived tumor samples (T#1 and T#2). (C) Comparison of the mRNA levels of the proinflammatory chemokines (Cxcl1 and Ccl2) between the TRAMP-C1 cell line and its derived tumor samples (T#1 and T#2). RT-qPCR measurements were derived from three technical replicates, and the results are presented as the mean ± SD. Student’s t-test. **** p < 0.0001. (D) Comparison of the cytokine/chemokine profiles of the LLC1 cell line and its derived tumors (T#1 and T#2). Differentially secreted factors are labeled with black arrows. (E) Comparison of the cytokine/chemokine profiles of the TRAMP-C1 cell line and its derived tumors (T#1 and T#2). Secretion of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL1RN) was increased in the tumors (white arrows).