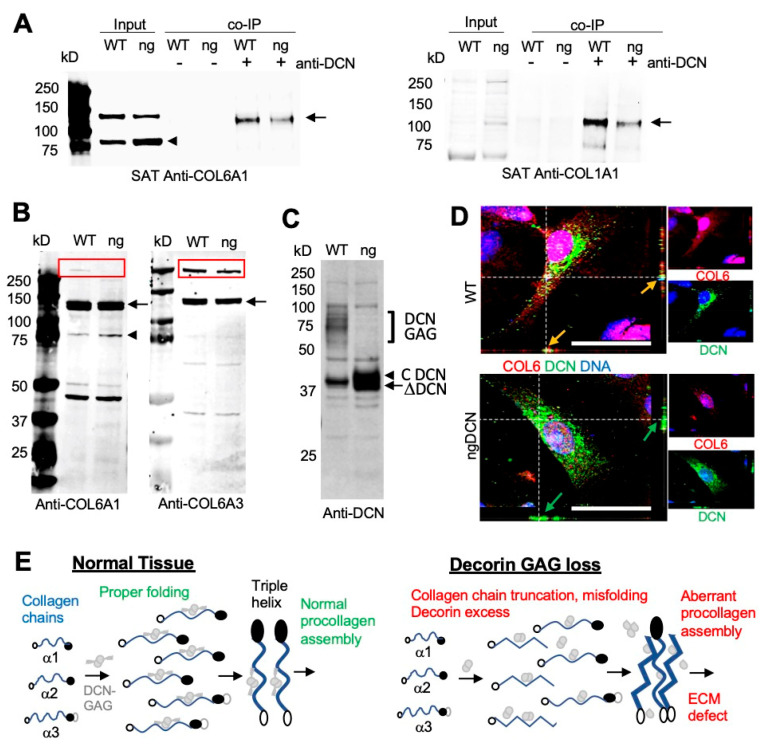
Figure 5.
Abnormal DCN binding and processing of collagen chains in ngDCN mice. (A) Anti-COL6A1 and anti-COL1A1 immunoblots of the protein extracts (Input) from SAT reveal a reduced level of full-length COL6A1 (arrow) and increased level of truncated COL6A1 (arrowhead) in ngDCN (ng) mice. Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) with anti-DCN IgG demonstrate less COL6A1 and COL1A1 chains (arrow) complexed with DCN in ngDCN mice. (B) Anti-COL6A1 and anti-COL6A3 immunoblots of protein extracts from WT and ngDCN (ng) adipocytes differentiated in cell culture after removal of ECM proteins. Note the increased formation of a truncated COL6A1 fragment (arrowhead), reduced levels of COL6 chains (arrow), and reduced levels of COL6 procollagen (box) migrating at ~500 kDa. (C) Anti-DCN immunoblots of the protein extracts reveal the lack of glycanated DCN and increased levels of non-glycanated DCN in lysates of ngDCN MEFs differentiated into adipocytes. (D) Confocal immunolocalization of DCN and COL6A1 in cultured primary ASC. Z-stack projections of median series reveal the change in COL6A1 distribution and reduced DCN colocalization in ngDCN cells. Scale bar = 50 µm. (E) A model depicting the role of DCN GAG in collagen fibrillogenesis. The glycanated DCN dimer binds to the three collagen VI chains and organizes their correct folding for proper procollagen formation. Lack of GAG on DCN results in increased DCN expression and collagen chain C-terminal truncation, which leads to elevated assembly of aberrantly folded procollagen and fibrosis.