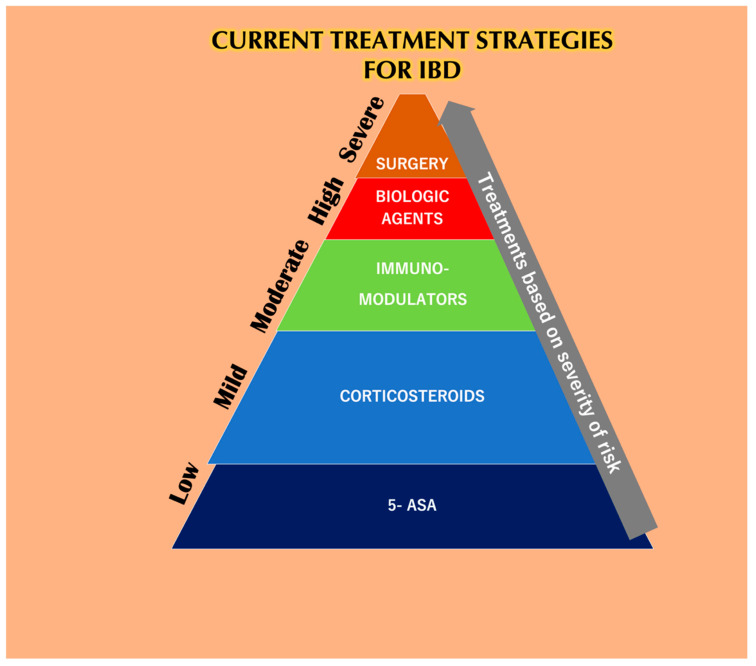
Figure 4.
The current treatment strategies for IBD depends solely upon the severity of the disease. At lower stages of IBD, 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) helps reduce the symptoms, but not for a prolonged period because it has a reduced bioavailability. Corticosteroids are also prescribed to IBD patients in the initial stages but are burdened with systemic toxicities. Immuno-modulators are used during moderate cases of IBD but have been reported to be linked with various side effects and also lead to the risk of developing lymphoma. Biological agents like anti-TNF- agents are used when patients are least responsive to the previous methodologies. Unfortunately, these agents are also responsible for various side effects when taken alone or as a combination with other mentioned therapies. Finally, IBD patients associated with dysplasia or cancer who undergo surgery also have a chance of relapsing [123].