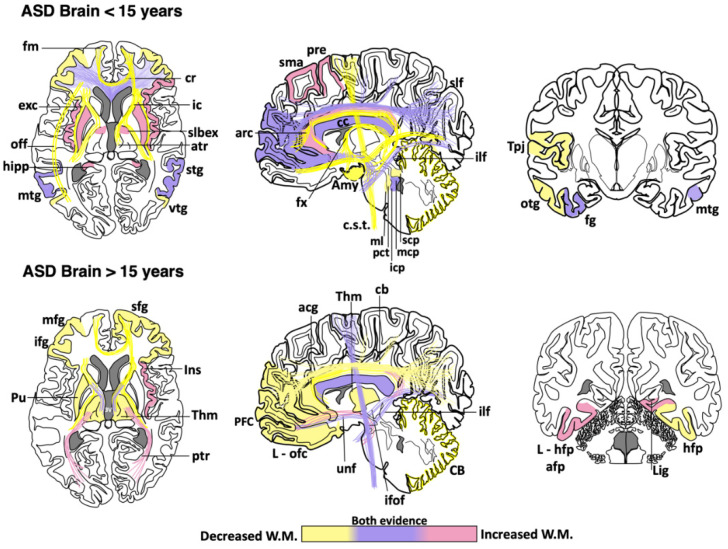
Figure 1.
Cortical areas, subcortical areas and white matter tracts affected in patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). White matter areas with the most noticeable changes are represented in the three anatomical planes of the human brain: axial, sagittal, and coronal, respectively. Brain schemes also indicate the most common myelination changes that occur in ASD patients during two different stages of development [21,30,36,60,64,65,67,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109]. acg: anterior cingulate gyrus; afp: amygdala-fusiform pathway; Amy: amygdala; atr: anterior thalamic radiation; arc: arcuate fasciculus; CB: cerebellum; cb: cingulum bundle; cc: corpus callosum; c.s.t.: corticospinal tract; cr: corona radiata; exc: external capsule; fm: forceps minor; fx: fornix; fg: fusiform gyrus; hipp: hippocampus; icp: inferior cerebellar peduncle; ifof: inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus; ifg: inferior frontal gyrus; Ins: insula; ic: internal capsule; L-hfp: left hippocampus-fusiform pathway; L-ilf: Left inferior longitudinal fasciculus; L-ofc: left orbitofrontal cortex; lig: lingual gyrus; ml: medial lemniscus; mcp: middle cerebellar peduncle; mtg: middle frontal gyrus; mtg: middle temporal gyrus; off: occipitofrontal fasciculus; otg: occipitotemporal gyrus; pct: pontine crossing tracts; ptr: posterior thalamic radiation; pre: precentral area; PFC: prefrontal cortex; Pu: putamen; slbex: sub-lobar extranuclear area; scp: superior cerebellar peduncle; sfg: superior frontal gyrus; slf: superior longitudinal fasciculus; stg: superior temporal gyrus; sma: supplementary motor area; Tpj: temporoparietal junction; Thm: thalamus; unf: uncinate fasciculus; vtg: ventral temporal gyrus.