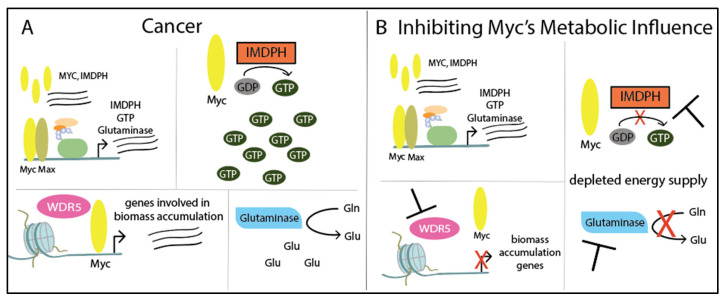
Figure 7.
Myc influences metabolism through its target genes: (A) In cancer, MYC overexpression correlates with IMPDH expression and transcribes other target genes, including GTP and glutaminase (GLN). IMPDH catalyzes GDP to GTP and glutaminase converts glutamine (Gln) to glutamate (Glu), a major energy source in cancer. Lastly, epigenetic co-factor WDR5 recruits Myc to chromatin to express genes involved in biomass accumulation. (B) Although Myc still has control over target genes IMPDH, GTP, and GLN, the function of these proteins can be inhibited. Cancer’s energy supply can be depleted by inhibiting IMPDH, which prevents GTP production, or by inhibiting glutaminase, which will limit the pool of glutamate. Finally, inhibiting WDR5 will prevent Myc’s target gene expression of biomass related genes.