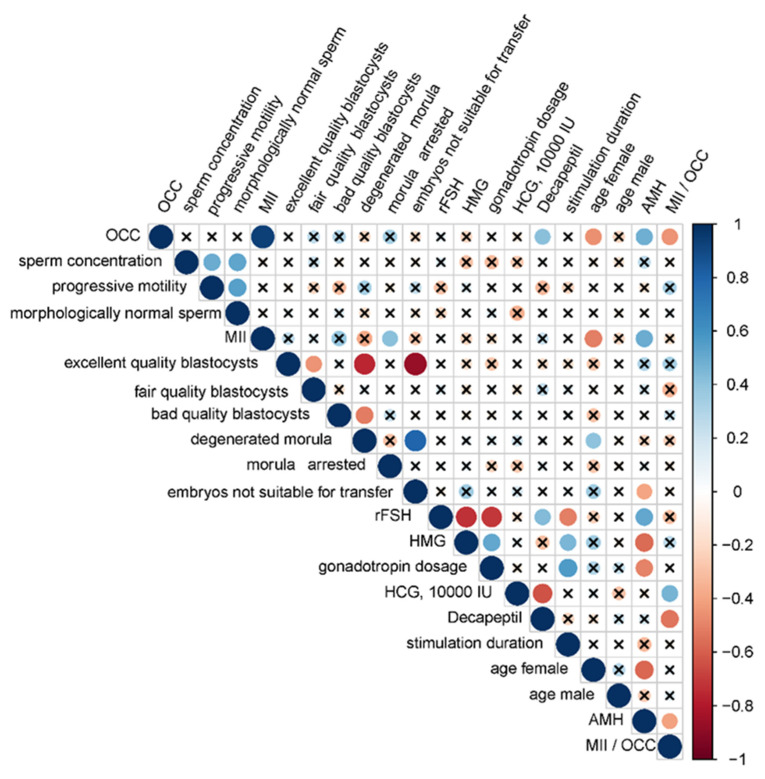
Figure 1.
Correlation matrix based on the nonparametric Spearman rank correlation method. Significant (p < 0.05) correlations are indicated by a dot, nonsignificant correlations are indicated by a cross, positive correlations are marked in blue, and negative correlations in red: the more significant the correlation, the larger the dot size. Parameters used in correlation analysis: OCC—the number of oocyte–cumulus complexes from the female of each couple; sperm concentration—spermatozoid count per milliliter of ejaculate from the male of each couple; progressive motility—percentage of linearly motile spermatozoids from the male of each couple; morphologically normal sperm—percentage of morphologically normal spermatozoids from the male of each couple; MII—metaphase II oocyte number from the female of each couple; excellent quality blastocysts—percentage of excellent/good-quality blastocysts on day 5 a.f.; fair quality blastocysts—percentage of fair-quality blastocysts on day 5 a.f.; bad quality blastocysts—percentage of bad-quality blastocysts on day 5 a.f.; degenerated morula—percentage of degraded morula on day 5 a.f.; morula arrested—percentage of morula arrested in development on day 5 a.f.; embryos not suitable for transfer—percentage of degraded morula, morula arrested in development and morula developed into a blastocyst of bad quality on day 5 a.f.; rFSH—the use of recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone for ovarian stimulation; HMG—the use of human menopausal gonadotropins for ovarian stimulation; gonadotropin dosage —total dose of gonadotropin used for ovarian stimulation, IU; HCG, 10,000 IU—the use of human chorionic gonadotropin (10,000 IU) for triggering final oocyte maturation; Decapeptil—the use of 0.2 mg decapeptyl for triggering final oocyte maturation; stimulation duration—duration of ovarian stimulation, days; AMH—the anti-Müllerian hormone level (ng/mL) in blood from the female of each couple; MII/OCC—metaphase II oocyte number as a percentage of oocyte–cumulus complexes.