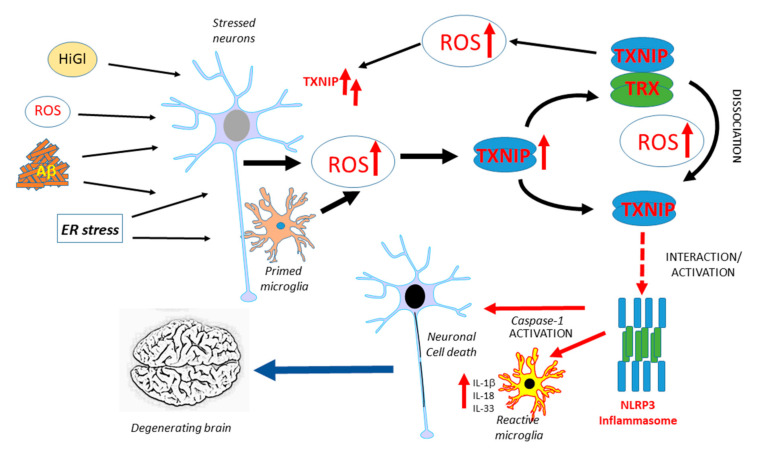
Figure 1.
Overview of features of TXNIP expression and function that might contribute to AD pathogenesis. Multiple factors have been identified to be possible initiators of AD-related neurotoxicity, all of which have been shown to induce TXNIP. The potential interactions leading to enhanced inflammation and neurodegeneration are illustrated. ROS: reactive oxygen species, HiGl: High glucose, ER: endoplasmic reticulum, TXNIP: thioredoxin-interacting protein, TRX: thioredoxin, IL: interleukin.