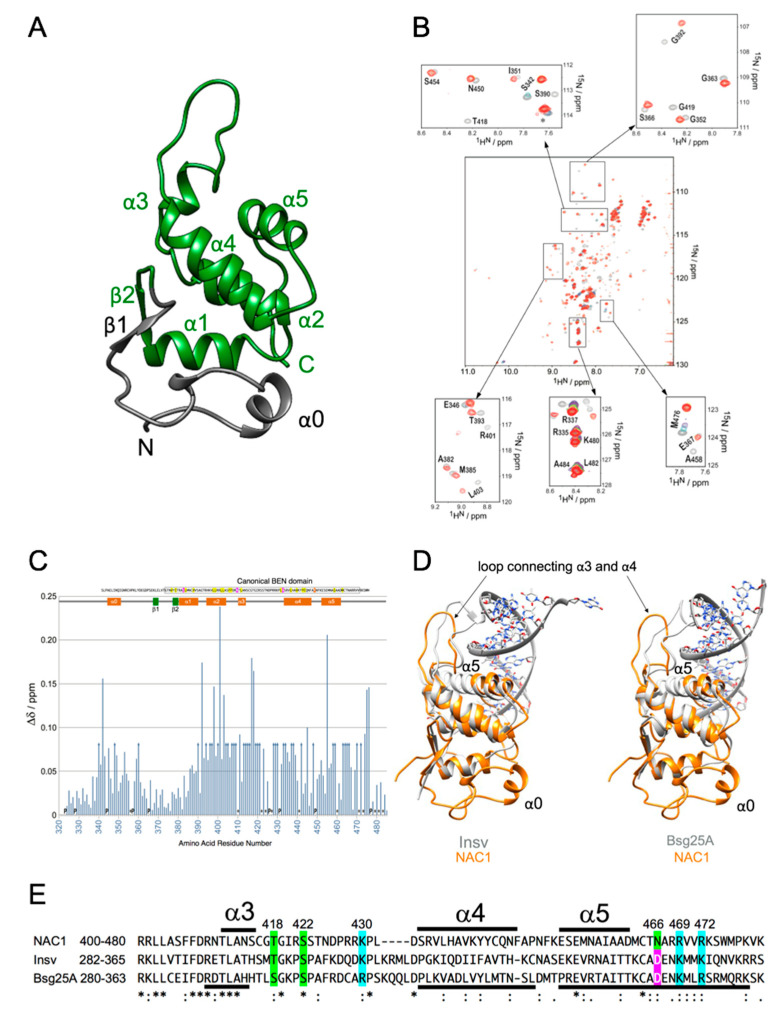
Figure 3.
NMR experiments of NAC1. (A) Ribbon representation of the lowest-energy solution structure of the BEN domain from human NAC1 (residues 322–485), determined by NMR spectroscopy. The secondary structure elements are shown with arrows (β-strand) and helices (α-helix). The predicted BEN domain is colored green. (B) NMR titration experiments of NAC1 with the NAC1 consensus dsDNA oligonucleotide. Overlay of the 1H–15N HSQC spectra of NAC1(322-485) alone (grey) and in the presence of 0.2 (purple), 0.4 (cyan), 0.6 (magenta), 0.8 (green), 1.0 (yellow), 1.2 (pink), and 1.5 (red) equivalents of dsDNA oligonucleotide. The five insets show peaks that disappeared or gradually changed position (from grey to red) in selected spectral regions upon the addition of dsDNA oligonucleotide. (C) Total changes in 1HN and 15N chemical shifts (Δδ) for NAC1(322-485) upon the addition of dsDNA oligonucleotide to a ratio of [protein]:[dsDNA] = 1:1.5 are plotted versus residue number. Δδ is given by Δδ = [(ΔδHN)2 + (ΔδN/6.5)2]1/2, where ΔδHN and ΔδN are the chemical shift differences for 1HN and 15N, respectively. Residues that were not assigned (asterisks) or whose 1H-15N resonances disappeared upon the addition of dsDNA oligonucleotide (arrows) are indicated. “P” indicates proline residues. Highly conserved residues of human BEN domain-containing proteins identified by Clustal Omega alignment are highlighted and shown at the top of the plot. See Figure 1A. The canonical BEN domain is boxed. Color coding reflects the conservation of amino acid types: yellow and magenta for hydrophobic and negatively charged amino acids, respectively. (D) Structural alignment of the BEN domain of human NAC1 and Drosophila BEN-solo proteins. NAC1 (322-485) is shown as a gold ribbon, and the Insv-BEN domain with dsDNA (PDB ID: 4IX7) (left panel) and Bsg25A (Elba1) with dsDNA (PDB ID: 4 × 0 G) (right panel) are shown in grey. (E) Clustal Omega alignment of the BEN domains of human NAC1, Drosophila Insv and Drosophila Bsg25A proteins. Color coding reflects the conservation of amino acid types: green, blue and magenta for hydrophilic, positively and negatively charged amino acids, respectively. Symbols are as follows: (*), identical residues; (:), highly conserved residues; (.) lower but significant conservation between all members. The α-helical regions labeled above are based on Figure 3A and those labeled below are based on PDB 4IX7 and 4 × 0 G. The source and corresponding UniProt accession numbers are indicated. NAC1, Q96RE7; Insv, Q8SYK5; Bsg25A (ELBA1), Q9VR17.