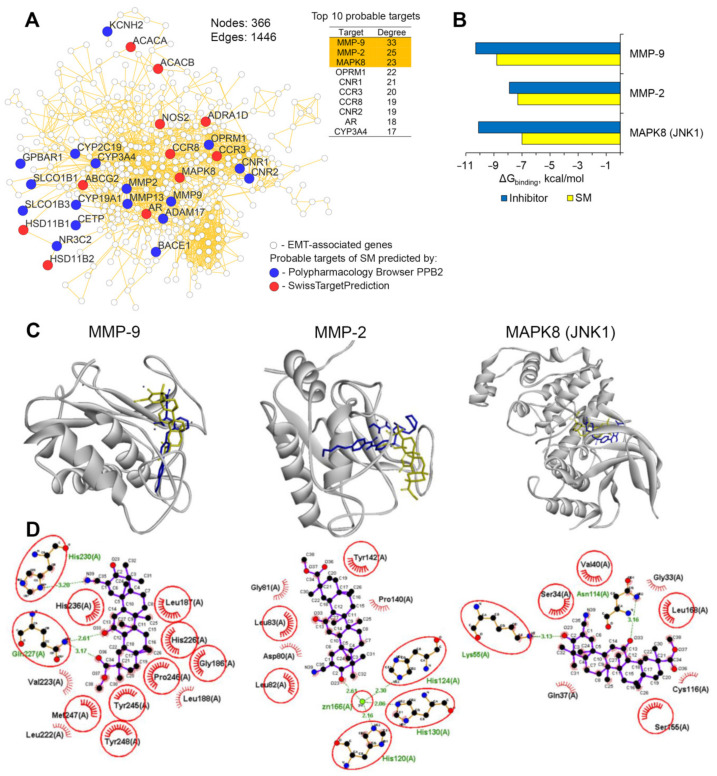
Figure 7.
Network pharmacology revealed c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase 1 (JNK1) and matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 (MMP-2/-9) as probable primary targets of SM, associated with its anti-EMT activity. (A) The gene association network consisted from EMT-related regulome and predicted SM’s protein targets was reconstructed using the STRING database (confidence score > 0.7) in Cytoscape. The top 10 interconnected probable targets of SM are listed in the table. Degree is the number of interconnections of analyzed node into the regulome. (B) The binding energies (ΔGbinding) of SM and the known inhibitors with the top 3 revealed EMT-associated probable targets of the triterpenoid calculated using Autodock Vina. (C,D) The mode of binding of SM to MMP-9, MMP-2 and JNK1. (C) 3D representation of docked poses of SM, superimposed on inhibitor bound structures of mentioned proteins was drawn by BIOVIA Discovery Studio. (D) 2D representation of docked poses of SM in MMP-9, MMP-2 and JNK1, created by LigPlot+. The green lines and red combs represent hydrogen bonds and non-bonding contacts, respectively. The amino acid residues, being commonly involved in the interaction networks of SM and the corresponding inhibitors are highlighted in red circles.