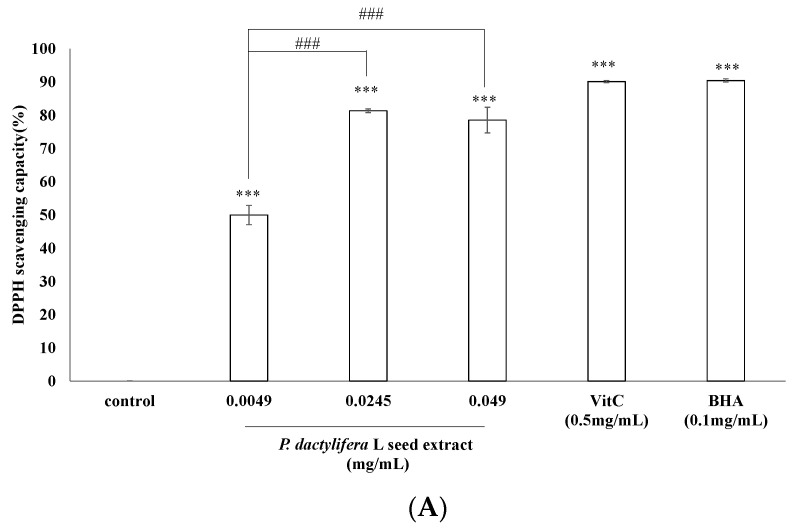
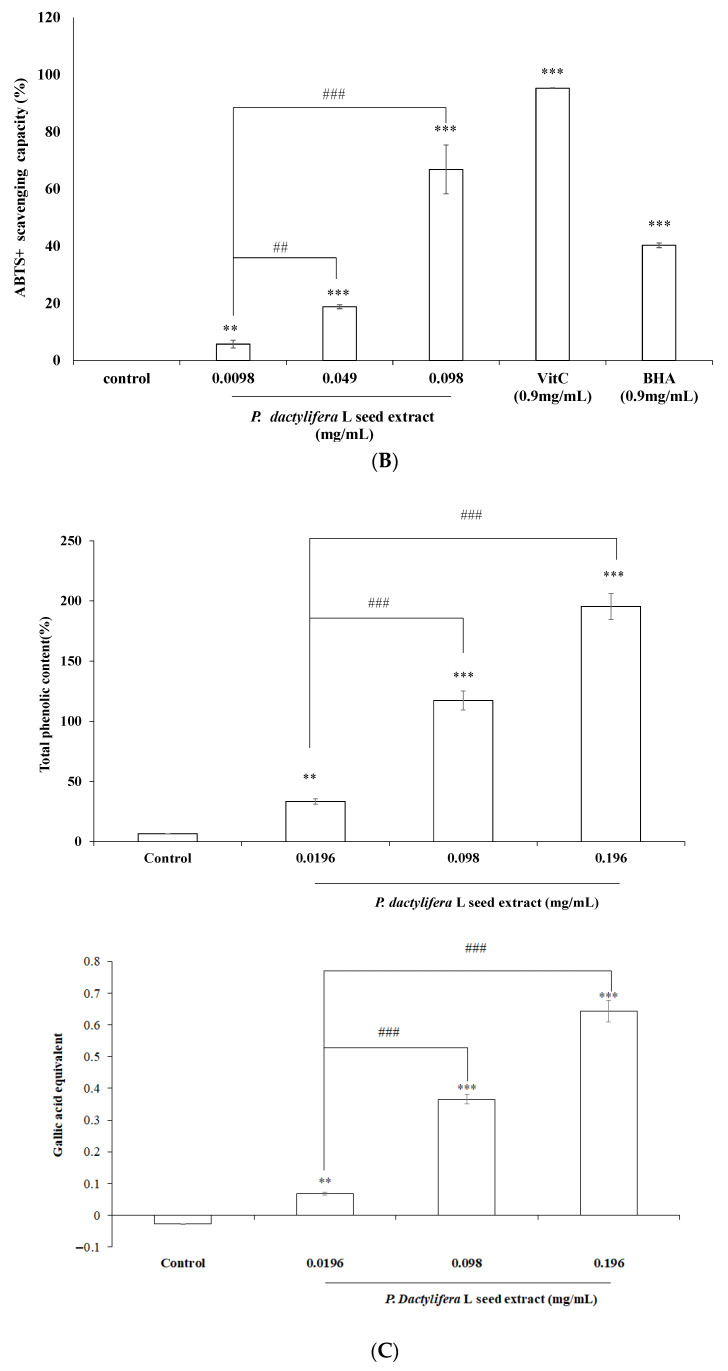
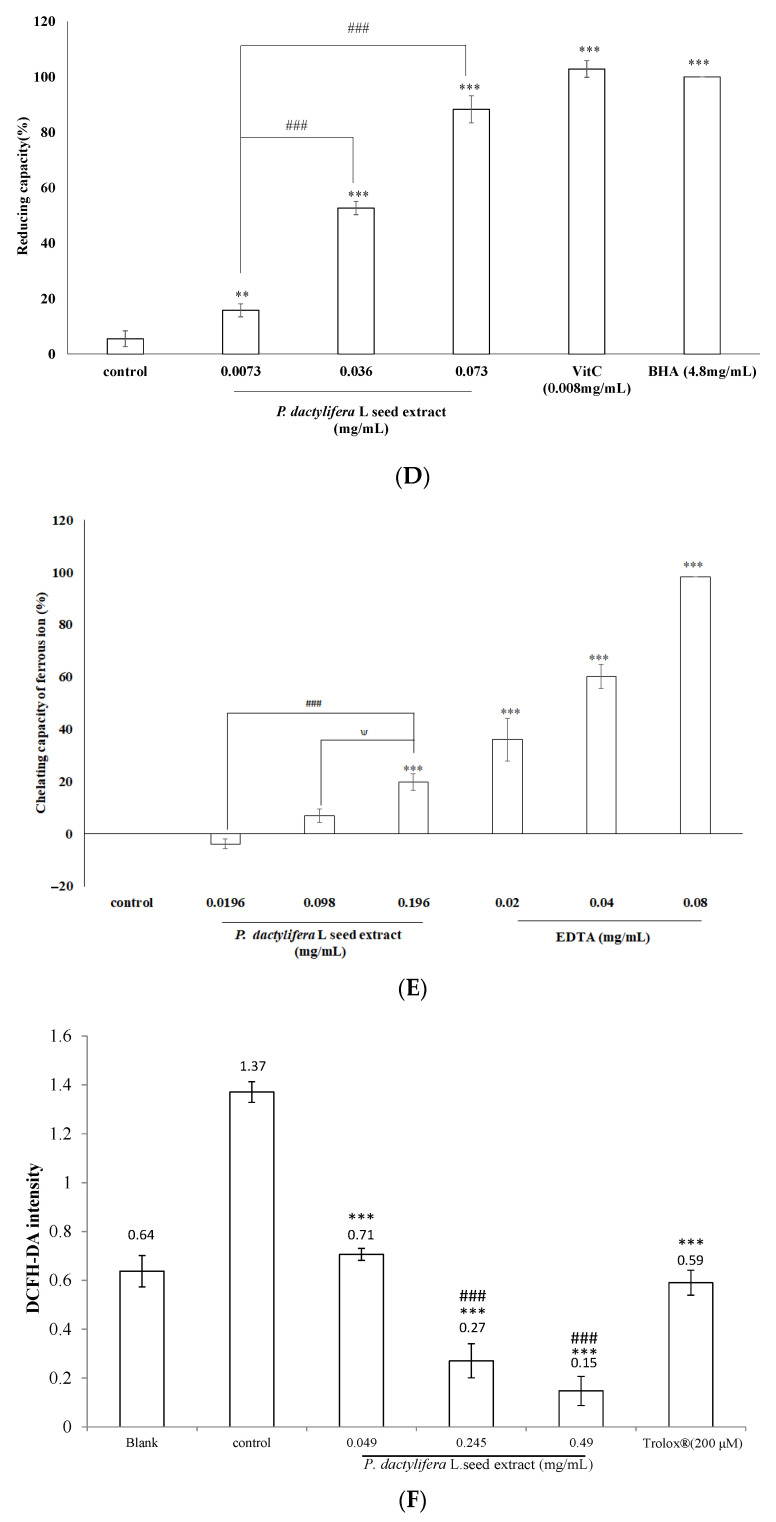
Figure 2.
Antioxidant characteristics of P. dactylifera L. seed extract. (A) DPPH assay. The extract at various concentrations (0.0049, 0.0245, and 0.049 mg/mL), vitamin C (0.53 mg/mL), or BHA (0.1 mg/mL) interacted with DPPH. The control was DPPH only. (B) ABTS+ assay. The ABTS+ scavenging capacity of the extract (0.0098, 0.049, and 0.098 mg/mL) was compared with those of vitamin C (0.9 mg/mL) and BHA (0.9 mg/mL). (C) Total phenolic content assay. Different concentrations of extracts were tested with the Folin–Ciocalteu reagent. The absorbance of samples was measured at 760 nm. (D) Reducing capacity assay. The absorbance at 700 nm of different concentrations of extract (0.0073, 0.036, and 0.073 mg/mL), vitamin C (0.008 mg/mL), and BHA (4.8 mg/mL) were measured. (E) Ferrous ion-chelating capacity assay. Different concentrations of extract (0.0196, 0.098, and 0.196 mg/mL) or the positive standard EDTA (0.02, 0.04, and 0.08 mg/mL) were added to a reaction solution. The absorbance of the reaction mixture was measured at 562 nm. (F) ROS assay. The B16F10 melanoma cells were pretreated with various concentrations of P. dactylifera L. seed extract (0.049, 0.245, and 0.49 mg/mL), Trolox® (0.05 mg/mL), or nothing for 24 h. The cells were then incubated with 24 mM H2O2 and DCFH-DA, and the fluorescence intensities of DCF were measured; the ROS levels were also calculated. Results are represented as percentages of control, and the data are mean ± SD for three separate experiments. Values are significantly different by comparison with control. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; ## p < 0.05, ### p < 0.001 seed extract group comparison; ψ, p < 0.05 seed extract (0.098 mg/mL) vs. (0.196 mg/mL).