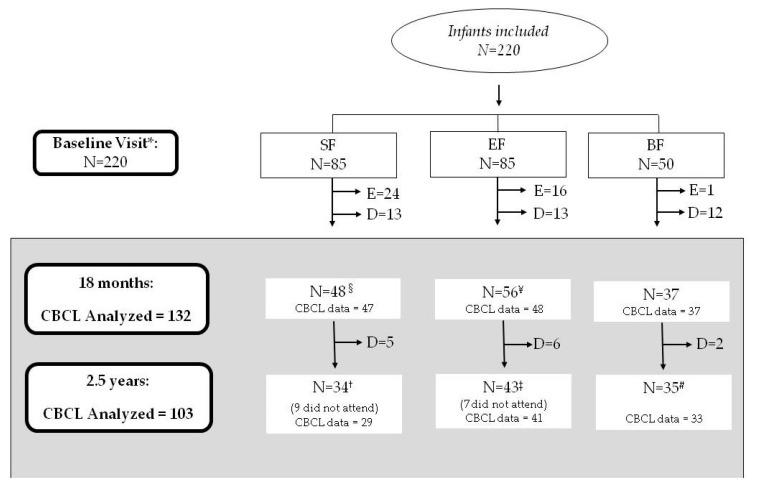
Figure 1.
Participant flowchart from recruitment to 2.5 years old. SF, standard infant formula; EF, experimental infant formula; BF, breastfed infants; D, drop-outs; E, exclusions, N, sample size. Up to 18 months of life, a total of 40 infants were excluded in the SF and EF groups as follows: 24 were excluded in the SF group (1 infant due to perinatal hypoxia, 1 infant had growth deficiency, 15 infants met the withdrawal criteria referring to formula intake, 2 infants were colic, 3 were excluded due to lactose intolerance, 1 infant was due to digestive surgical intervention, and 1 infant suffered hydrocephalus); 16 infants were excluded in the EF group (2 infants presented growth deficiency, 2 infants lactose intolerance, 11 infants met the withdrawal criteria referring to formula intake, and 1 was excluded due to epileptic seizure). Furthermore, one infant of the BF group was excluded because they were not breastfed. * BF infants were randomized between 0–6 months of age. § 1 mother did not fill the child behavior checklist (CBCL) test at 18 months old; ¥ 8 mothers did not complete the CBCL test at 18 months old; † 5 mothers did not fill the CBCL test at 2.5 years old; ‡ 2 mothers did not fill the CBCL test at 2.5 years old; # 2 mothers did not complete the CBCL test at 2.5 years old. Sixteen children at 2.5 years old did not show up at the evaluation (described as “did not attend”). During the follow-up visit at 18 months, dropouts were considered those who did not continue to participate in the study: mainly due to not wanting to continue in the study or not being able to come to the follow up visits, usually for a change in place of residence or workplace conditions of the parents.