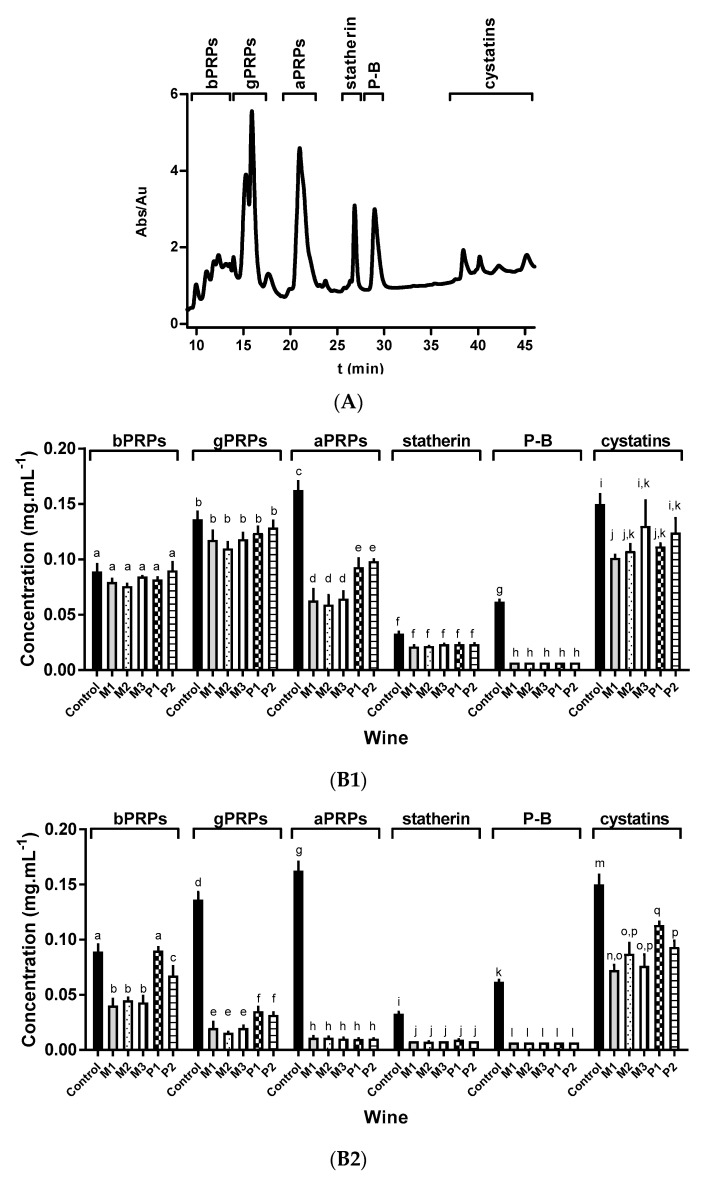
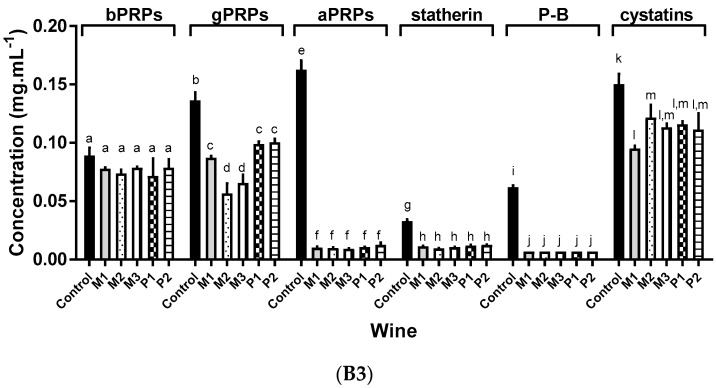
Figure 2.
(A) Typical salivary protein profile obtained by HPLC analysis with detection at 214 nm, and identification of the major families eluted along the chromatogram, the identification of the different families has been previously reported [22,37]; bPRPs: basic proline-rich proteins, gPRPs: glycosylated proline-rich proteins, aPRPs: acidic proline-rich proteins. (B) Modifications in the concentration (mg mL−1) for each family of salivary proteins upon the interaction with each wine (two bottles of M wine (M1 and M2) and three bottles of P wine (P1, P2, and P3)) at different ratios (B1) 10:0.7, (B2) 10:2, and (B3) 10:3. Control condition is the concentration of each family of salivary proteins in human saliva in the absence of wine. Data are presented as mean and SEM of at least three independent experiments (values with the same letter are not significantly different, p < 0.05, ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons).