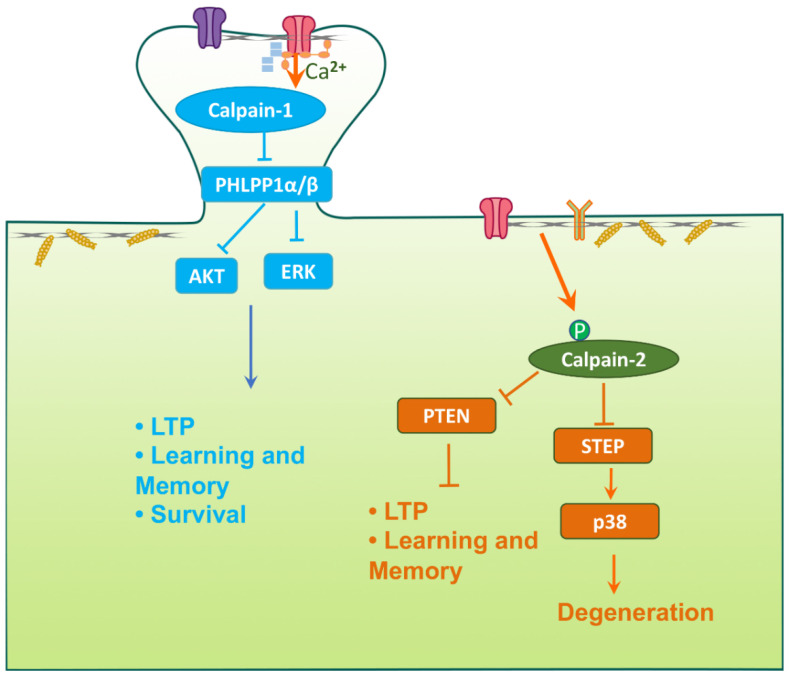
Figure 6.
Different subcellular locations and functions of calpain-1 and calpain-2 in excitatory neurons. Calpain-1 is preferentially linked to synaptic N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) receptors while calpain-2 is downstream of extra-synaptic NMDA receptors in neurons. Synaptic NMDAR activation activates calpain-1, which cleaves and inhibits PHLPP1α/β. PHLPP1α/β inhibits AKT and ERK. Thus, calpain-1-mediated cleavage of PHLPP1 activates AKT and ERK, which trigger long-term potentiation (LTP) and promote neuronal survival. On the other hand, extra-synaptic NMDAR activation induces phosphorylation and prolonged activation of calpain-2. Calpain-2 cleaves its substrates such as PTEN and STEP, leading to reduced LTP magnitude and neurodegeneration.