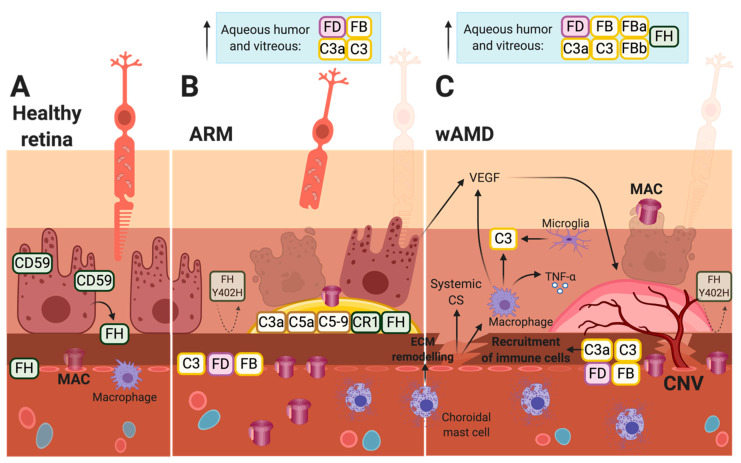
Figure 4.
Patient samples reveal increased complement deposition in ARM and AMD eyes. (A) The healthy human retina is protected from the complement system by Factor H and CD59, and potential inflammatory immune cells are localized on the choroidal side of the outer blood–retina barrier (BRB). (B,C) Complement components are deposited in different compartments of the eyes in both ARM and wAMD patients. Loyet et al. found the highest level of complement deposition in the CC followed by Bruch’s membrane [52]. The RPE, macrophages, and complement system are involved in the production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and, thus, the formation of CNV. AP, alternative pathway. ARM, age-related maculopathy. BRB, blood–retina barrier. CC, choriocapillaris. CNV, choroidal neovascularization. CP, classical pathway. ECM, extracellular matrix. FB, Factor B. FD, Factor D. FH, Factor H. FI, Factor I. LP, lectin pathway. MAC, membrane-attack complex. PR, photoreceptor. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium. TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha. VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.