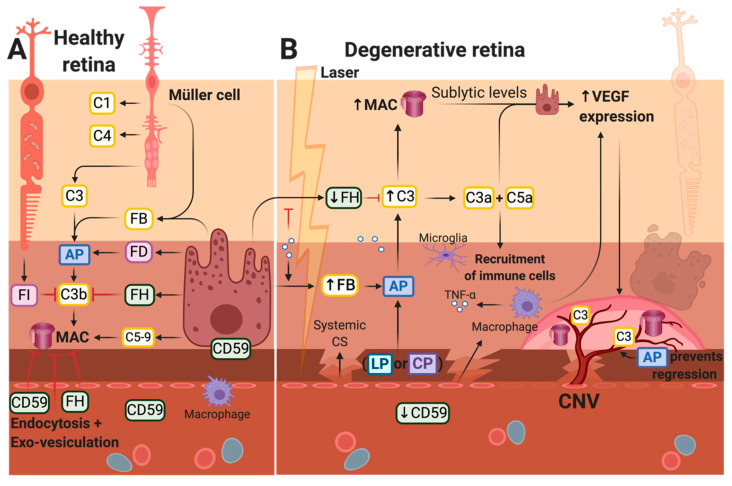
Figure 5.
In vitro and in vivo studies indicate important roles for the AP, MAC, and the anaphylatoxins in CNV-formation. (A) In the healthy retina, complement activation and MAC-deposition in the RPE cells and CC are kept in check by inhibitors such as FH, CD59, and endocytosis [126]. (B) Shortly after laser-induction, the level of anaphylatoxins was found to increase [140], i.e., the complement system was activated. RPE cells in close proximity to the laser may degenerate directly due to coagulation necrosis, the following scar-formation, or CNV detaching the RPE from its source of nutrition. The activation of the complement system is pronounced in several cell layers of the outer retina and in the choroid. Therefore, it is not restricted to the specific regions shown above. AP, alternative pathway. CC, choriocapillaris. CNV, choroidal neovascularization. CP, classical pathway. FB, Factor B. FD, Factor D. FH, Factor H. FI, Factor I. LP, lectin pathway. MAC, membrane-attack complex. PR, photoreceptor. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium. TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha. VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.