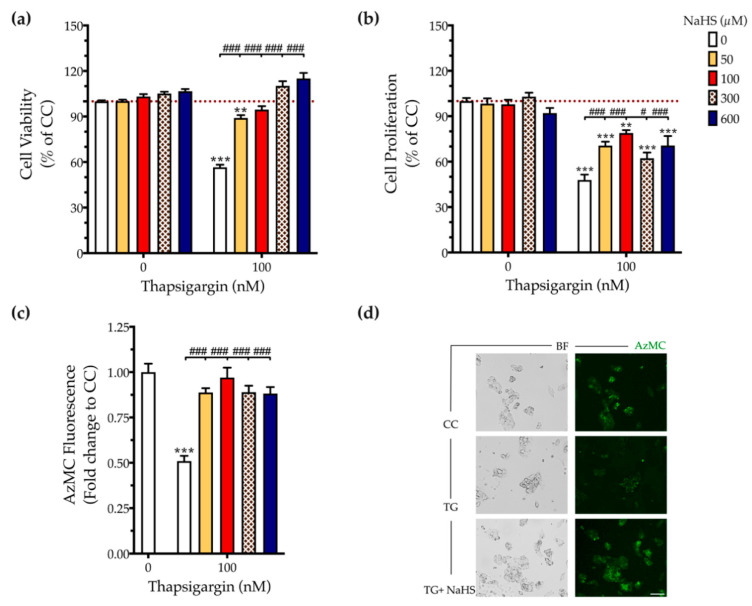
Figure 2.
NaHS co-treatment normalizes the endogenous H2S levels and rescues hepatic-cell viability and proliferation during chronic ER stress. HepG2 cells were serum-starved for 8 h and treated with the vehicle or 100 nM of thapsigargin (TG), in the presence or absence of NaHS for 16 h. Micro-cultures were assayed for the XTT conversion (a) and BrdU incorporation (b) to assess cell viability and proliferation, respectively. Alternatively, micro-cultures were labeled with 100 µM AzMC to quantify the endogenous H2S levels (c). Representative pictures of the AzMC signal were captured with an Olympus CKX53 inverted microscope at 10× magnification; the left sub-panel corresponds to the bright-field channel (BF) for whole-cell imaging, whereas the right sub-panel to the DAPI fluorescent channel for AzMC imaging (d). Each bar represents mean ± SEM from four independent experiments. Data are expressed as a percentage or fold change of the control (vehicle-treated) conditions (CC). ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001, when compared to CC; # p ≤ 0.05; ### p ≤ 0.001, when compared to the TG-treated HepG2 cells. Scale bar: 20 µm.