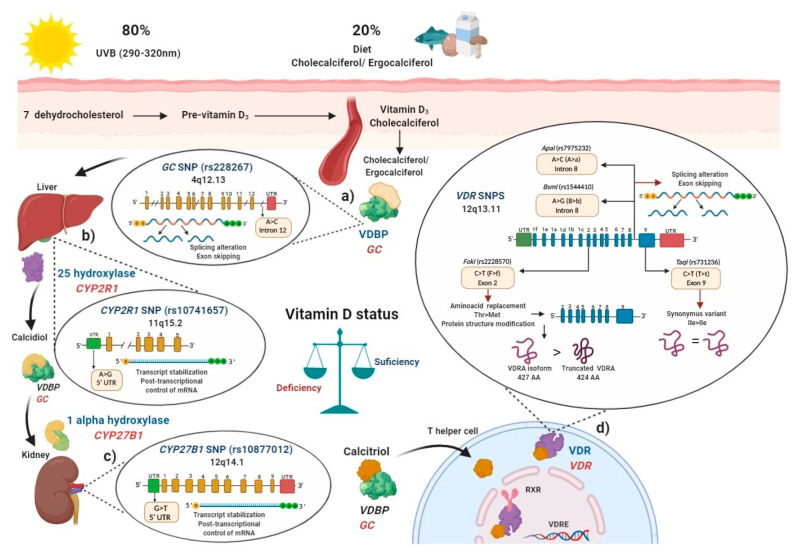
Figure 2.
Polymorphisms in main key enzymes and proteins associated with vitamin D metabolism: localization and functional effects: (a) Vitamin D binding protein (VDBP) (encoded by GC gene) binds to ergocalciferol/cholecalciferol in order to be transported to the liver; GC (rs2282679) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) due to its location in intron may generate a splicing alteration and exon skipping; (b) In the liver, 25 hydroxylase (encoded by CYP2R1 gene) converts ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol to calcidiol and then calcidiol binds to VDBP to be transported to the kidney; CYP2R1 (rs10741657)SNP located on the 5′ untranslated region (UTR) region may affect the transcript stabilization and the post-transcriptional control; (c) In the kidney, calcidiol is converted to calcitriol by the enzyme 1 alpha hydroxylase (encoded by the CYP27B1 gene); CYP27B1 (rs10877012) SNP located on 5′ UTR may affect the transcript stabilization and the post-transcriptional control of mRNA; (d) After calcitriol enters target cells and binds to vitamin D receptor (VDR) (encoded by VDR gene). Then, the VDR-calcitriol complex in the cytosol is translocated to the nucleus, where it binds to retinoid X receptor (RXR) to form a heterodimer, which interacts with vitamin D response element (VDRE) in vitamin D target genes, i.e., in T helper (Th) lymphocytes to suppress IL-17A or activate FOXP3. Mainly four SNPs have been described in the VDR gene: the FokI (rs2228570) located on exon 2, which generates a non-synonymous polymorphism with a change of C > T (also called F > f) and this results in a change of threonine to methionine. The presence of the restriction site FokI C allele (F allele), generates a new start codon (ATG) 9 bp after of the common starting site, which translate to an shorter truncated VDR protein of 424 amino acids with more transactivation capacity as a transcription factor than the wild type full-length VDR A isoform (VDRA) of 427 amino acids; the BsmI (rs1544410) located on intron 8 presents a change of A > G (also called B > b), could affect messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) stability and the gene expression of VDR, and also it could generate an alteration in the splice sites for mRNA transcription or a change in the intron regulatory elements of VDR; ApaI (rs7975232) located on intron 8 of VDR presents a change of A > C (also called A > a), does not change the amino acid sequence of the VDR protein, therefore could affect mRNA stability and the gene expression of VDR; TaqI (rs731236) is located on the exon 9 of VDR, presents a change of C > T (also called T > t) and generates a synonymous change of the isoleucine amino acid in the coding sequence, therefore it does not change the encoded protein, but it could influence the stability of the mRNA. All these SNPs are related to modulating de vitamin D serum status in health and disease. Ile: isoleucine; Thr: threonine; Met: methionine VDBP: vitamin D binding protein; VDR: vitamin D receptor; RXR: retinoid X receptor; VDRE: vitamin D response elements; UTR: untranslated region; THEM4: thioesterase superfamily member 4; Th: T helper lymphocyte; VDRA: wild type full-length VDR A isoform.