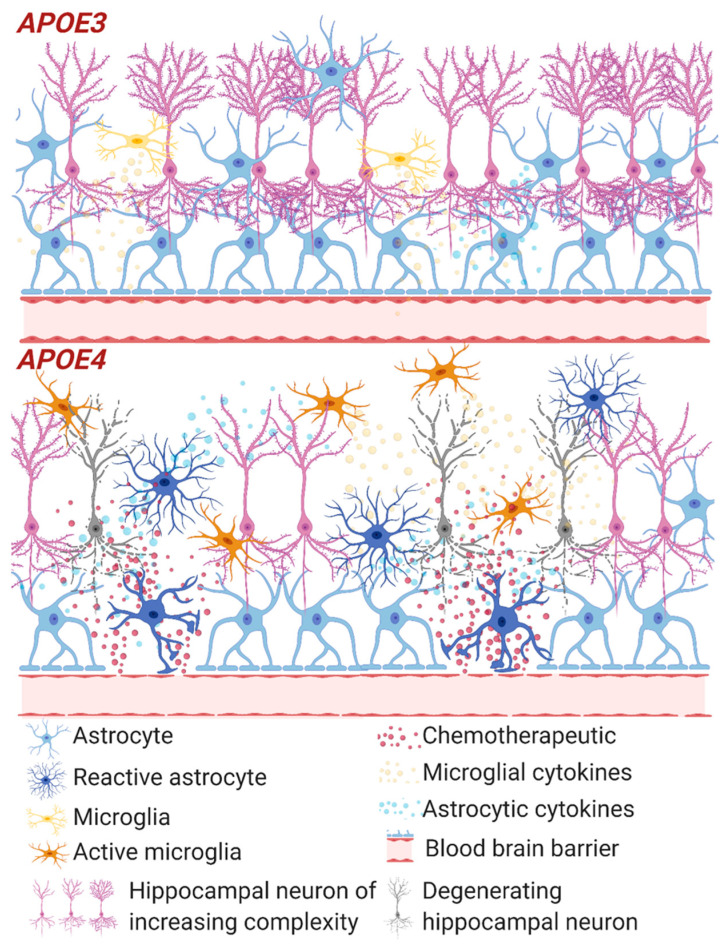
Figure 1.
Inflammation and the blood brain barrier with chemotherapy. Summary of impacts of chemotherapeutics on APOE3 and APOE4 neural tissue and the blood brain barrier (BBB). APOE4 show thinning basement membrane and impaired tight junctions leading to increased BBB permeability and release of chemotherapeutic (red particles) into the brain compartment, not apparent in APOE3. This impairment leads to increasing the already heightened immune and oxidative stress response in APOE4, increasing reactive astrocytes and active microglia, further increasing BBB breakdown. Ultimately this results in an environment that increases neurodegeneration (grey neurons). Although chemotherapeutic agents are unable to cross the secure APOE3 BBB, they are still able to induce a cytokine response close to the BBB which may damage the integrity of the tight junctions.