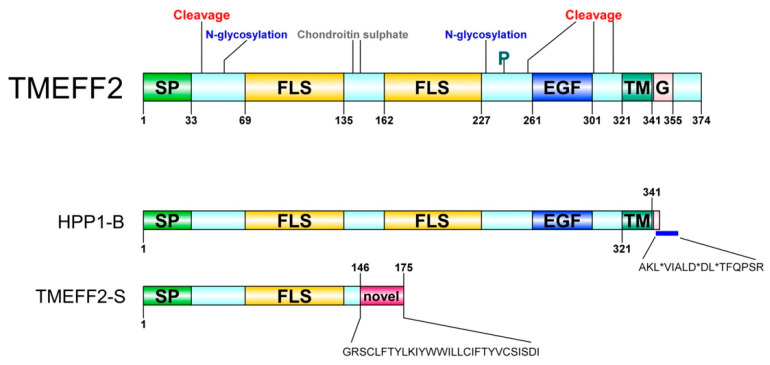
Figure 1.
Transmembrane protein with an EGF-like and two Follistatin-like domains 2 (TMEFF2) protein architecture. SP: signal peptide, FLS: follistatin-like domain, EGF: EGF-like domain, TM: transmembrane domain, G: G-protein activating motif, P: phosphorylation site. A Ser/Gly rich region between the two follistatin-like domains constitutes a glycosaminoglycans (chondroitin sulphate) attachment site. A potential Tyr kinase phosphorylation site at residue 242, N-linked glycosylation sites around residues 55 and 203, and several potential protease cleavage sites (only shown cleavage sites reported through hydropathy analysis) are represented. HPP1-B is a less frequently isolated TMEFF2 variant originating from a 57-bp sequence insertion in its gene. The new sequence following the transmembrane domain contains three stop codons resulting in a truncated protein short of its cytoplasmic tail; stop sites are marked with *. TMEFF2-S is a short isoform where the first 146 residues of TMEFF2 are followed by a 29-residue long novel sequence. Imaging software: DOG [9].