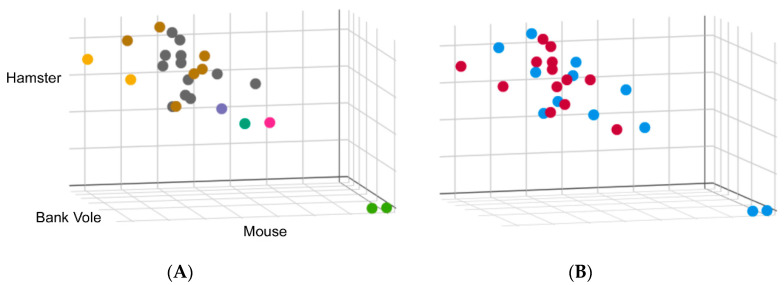
Figure 3.
Real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QuIC) was performed on 10−4 dilutions of brain homogenate from 25 cases of sCJD using 3 different substrates: full-length mouse, hamster and bank vole. Conversion rate was measured by comparing the time at which fluorescence in a given reaction exceeds a pre-defined threshold, i.e., the lag phase. Lag phases for each case were normalized to a 263 K hamster brain homogenate run concurrently as a standard to allow direct comparison between each run. These values were plotted on a scatter plot where the axes represent the normalized lag phase for each substrate. (A) Cases were colored according to the biochemical subtypes: Type 1, shown in grey, and Type 2, shown in brown. Two cases where a mixture of Type 1 and Type 2 were identified are shown in yellow. Cases shown in green are two cases of variably protease sensitive prionopathy (VPSPr). A Type 1 case with a biochemically distinct denaturation profile is shown in green and two others that do not exhibit typical glycoform patterns by Western blot shown in pink and purple. (B) Data were colored to reflect RT-QuIC seeding from brains of CJD patients, with or without exposure to venison, shown as blue or red, respectively.