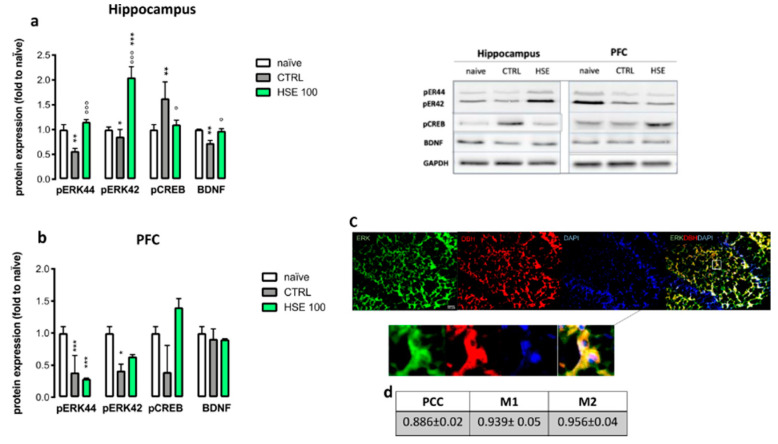
Figure 5.
(a) Helichrysum stoechas Moench methanolic extract (HSE) increased the phosphorylation of ERK44 in the hippocampus (one-way ANOVA post-hoc Tukey, F(2,6 = 57.14) ** p < 0.01 vs. naïve; °°° p < 0.001 vs. CTRL) and ERK42 (one-way ANOVA post-hoc Tukey, F(2,6 = 56.88), *** p< 0.001 * p < 0.01 vs. naïve; °°° p < 0.001 vs. CTRL) compared to naïve (mice without anxiety-like symptoms) and CTRL (mice with anxiety-like symptoms). HSE reduced the pCREB (one-way ANOVA post-hoc Tukey, F(2,6 = 8.157), ** p < 0.01 vs. naïve; ° p < 0.05 vs. CTRL) and increased BDNF (one-way ANOVA post-hoc Tukey, F(2,6 = 43.47), ** p < 0.01 vs. naïve; ° p < 0.05 vs. CTRL) compared to the CTRL group. (b) HSE did not show any effects on p-ERK42/44 in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) (one-way ANOVA post-hoc Tukey, F(2,6) = 37.98, *** p < 0.001 * p < 0.05 vs. naïve), pCREB (one-way ANOVA post-hoc Tukey, F(2,6) = 11.65)) and BDNF (one-way ANOVA post-hoc Tukey, F(2,6) = 11.0.766) protein levels, compared to the CTRL group. Representative micrograph showing ERK (green), DBH (red), DAPI (blue) and merge (c). Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC) and M1/M2 values are reported in the table (d). The vertical bars represent ± SD (n = 3). Representative blots are reported.