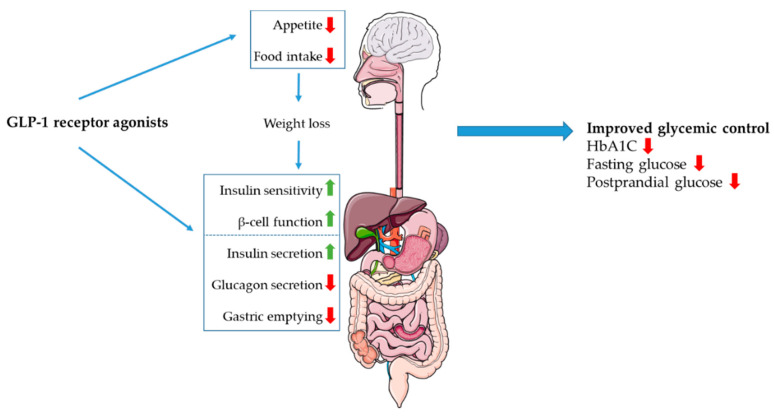
Figure 2.
The central and peripheral effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists are shown in this diagram. GLP-1 receptor agonists have shown to reduce food intake and appetite in various degrees. This results in weight loss, which enhances the positive effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on insulin sensitivity and β-cell function. Furthermore, administration of GLP-1 receptor agonists enhances insulin secretion, whilst inhibiting glucagon secretion and gastric emptying. This results in improved glycemic control in treated patients, as indicated by reduced Hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) and fasting glucose levels.