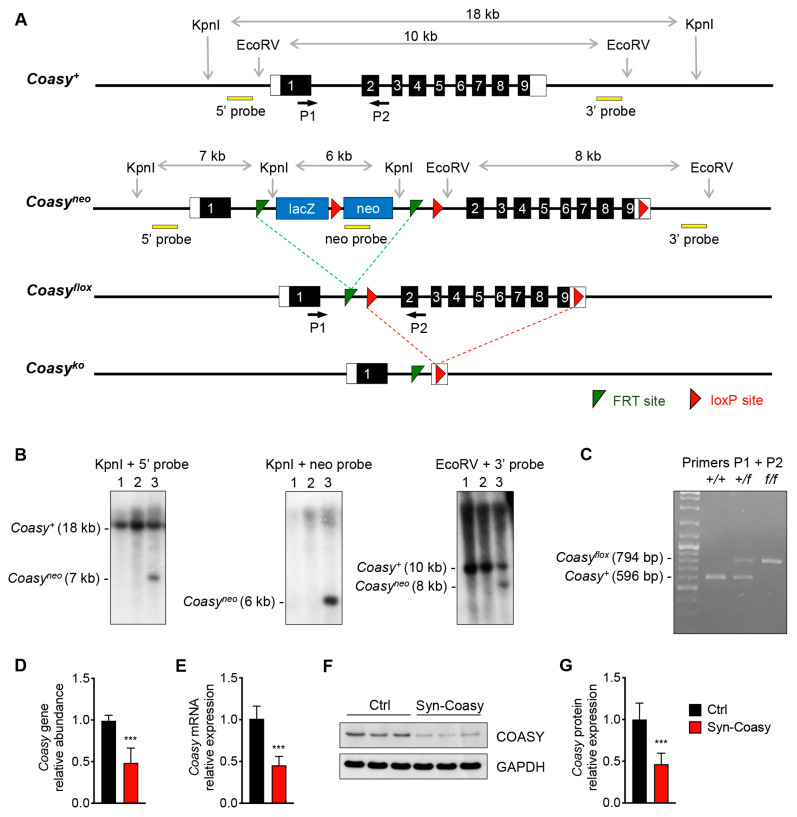
Figure 1.
Generation of Cre-loxP Coasy transgenic mice. (A) A schematic diagram of the Coasy wild-type locus (Coasy+) Homologous recombination of the targeting construct resulted in production of the Coasyneo allele. By sequential mating with FLPE and Cre transgenic mice, Coasyflox and Coasyko alleles were obtained. The primers (black arrows) used for PCR genotyping, as well as the probes (yellow boxes) used for southern blot analysis are shown. (B) Southern blot analysis on KpnI/EcoRV-digested genomic DNA of ES cell clones with 5′, neo and 3′ probes, showing wild-type (Coasy+) and recombinant (Coasyneo) bands. Lane 1 and 2: Coasy+/+; lane 3: Coasy+/neo. (C) PCR genotyping strategy using primers P1 and P2 to distinguish the wild-type (Coasy+) and the floxed (Coasyflox) alleles on wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/f), and homozygous (f/f) recombinant mice. (D) Relative amount of Coasy gene in the brain of Ctrl (n = 8) and Syn-Coasy (n = 8), tested by RT-qPCR. (E) Relative Coasy mRNA expression in Ctrl (n = 8) and Syn-Coasy (n = 8) mice brain. (F) Western blot analysis and (G) densitometric quantification of Coasy in the brain from Ctrl (n = 8) and Syn-Coasy (n = 8) mice. GAPDH was used as the loading control. For (D,E,G), mean ± SD is shown. *** p < 0.001 (Student’s t-test).