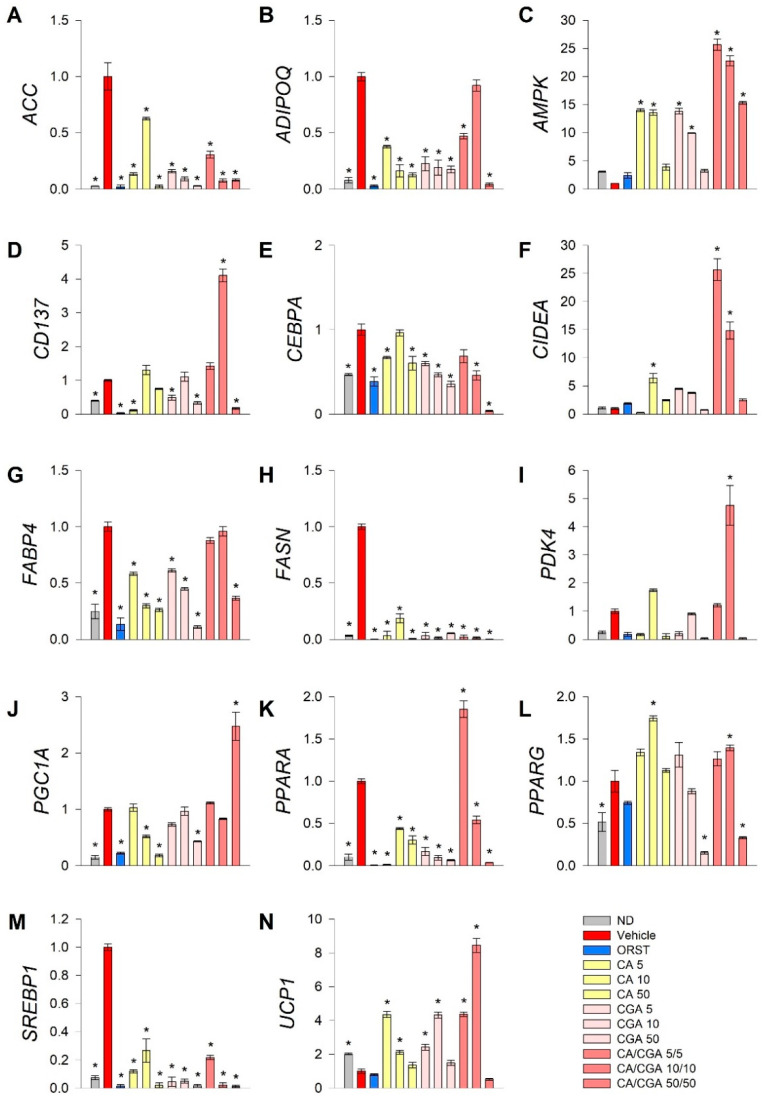
Figure 3.
Combined treatment with caffeic and chlorogenic acids altered adipogenic gene expression and induced browning markers’ transcriptional activation in human SGBS adipocytes. Relative mRNA expression (∆∆Cq) normalized to vehicle control group for the following genes: (A) acetyl-coA-carboxylase (ACC), (B) adiponectin (ADIPOQ), (C) AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), (D) tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 (CD137), (E) CAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA), (F) cell death activator CIDE-A (CIDEA), (G) fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4), (H) fatty acid synthase (FASN), (I) pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 4 (PDK4), (J) peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator 1 alpha (PGC1A), (K) peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARA), (L) PPARG, (M) sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1) and (N) uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) from the RT-qPCR. RPL13A and TUBB were applied as reference genes. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate from three independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05 compared to the vehicle control group.