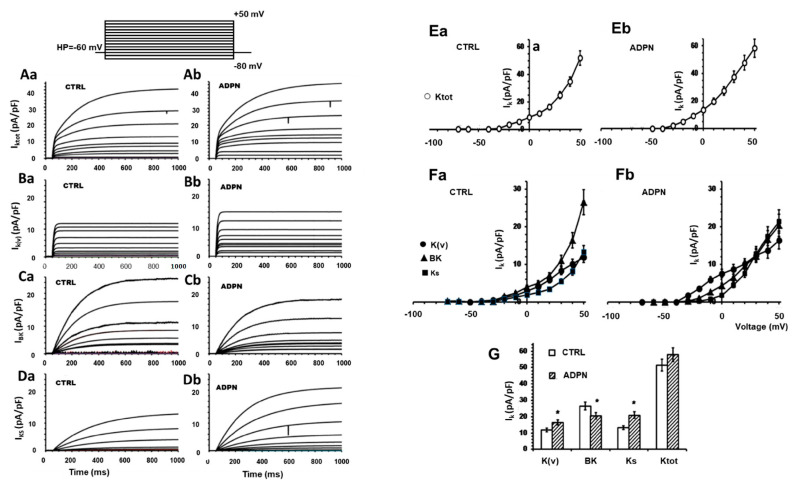
Figure 3.
Effects of ADPN on the different voltage-dependent K+ currents in an SMC from the gastric fundus. (Aa,Ab)Total outward K+ currents traces, elicited by voltage steps from −80 to +50 mV (holding potential (HP) = -60 mV) in nifedipine (10 μM) containing solution, in control condition (Aa), and in the presence of ADPN 20 nM (Ab). Current values are normalized to cell capacitance. The pharmacological dissection allowed us to systematically distinguish three kinds of K+ currents: IKv (Ba,Bb); IBK (Ca,Cb); and IKs (Da,Db). Current values are normalized to cell capacitance. (Ea,Eb) I–V plots related to IK,TOT in CTRL (Ea) and in the presence of ADPN (Eb). (Fa,Eb) I–V plots related to IKV, IBK, and IKs, in CTRL conditions (Fa) and in the presence of ADPN (Fb). The continuous lines through the experimental data represent the fitted Boltzmann function. Current values are normalized to cell capacitance. Statistical significance is not depicted in the figure for clarity. (G) Bar charts representing the amplitude of K+ current for IK,TOT, IKV, IBK, and IKs, in CTRL conditions and in the presence of ADPN. Comparison of the maximal current values recorded at +50 mV; * p < 0.05 of ADPN vs. CTRL. All of the data are mean values ± SEM. In each experimental condition, data are from CTRL n = 30 cells, ADPN n = 9 cells (5 mice).