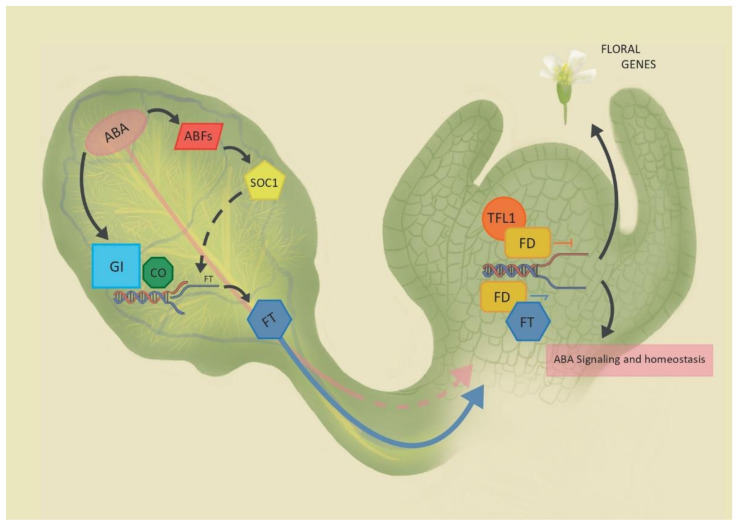
Figure 1.
Abscisic acid (ABA) signaling and flowering regulation. In the leaves (left), ABA controls FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) transcription acting on GIGANTEA (GI) and CONSTANS (CO); ABA-responsive transcription factors (ABFs) can modulate SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1 (SOC1) expression, in turn affecting FT transcription through an indirect mechanism. FT moves to the SAM where it interacts with FD and FD-like basic leucine zippers (bZIPs) to activate floral genes and ABA signaling transcriptome. ABA is transported in the phloem, but its roles at the SAM are not yet known. TERMINAL FLOWER 1 (TFL1) antagonizes FT, repressing transcription. Dashed lines represent indirect or not yet confirmed pathways, while full lines represent known ones.