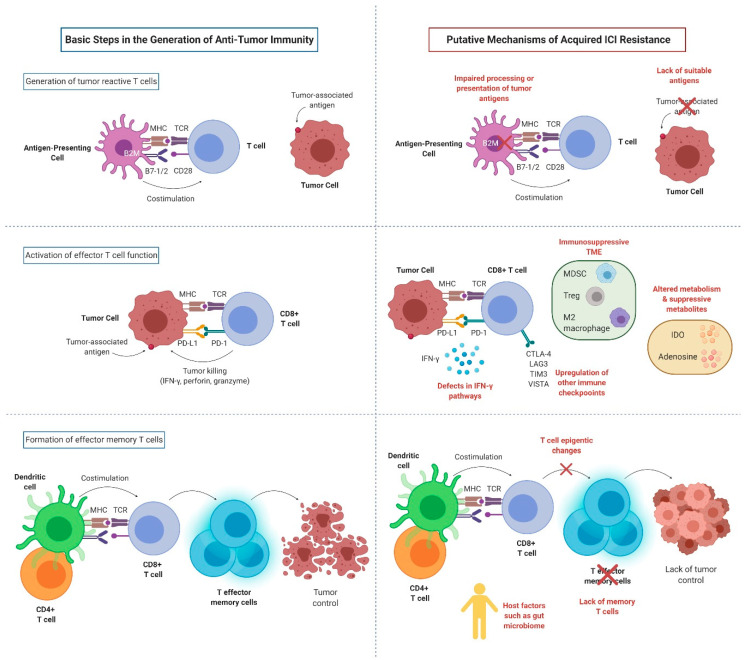
Figure 2.
Key mechanisms of acquired resistance to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors (created with BioRender.com). MHC: major histocompatibility complex; TCR: T cell receptor; CD28: cluster of differentiation 28; B7-1: cluster of differentiation 80; B7-2: cluster of differentiation 86; B2M: B2-microglobulin; PD-1: programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1: programmed death-ligand 1; IFN-γ: interferon gamma; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; LAG3: lymphocyte-activation gene 3; TIM3: T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing molecule 3; VISTA: V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation; MDSC: myeloid-derived suppressor cells; Treg: regulatory T cell; IDO: indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.