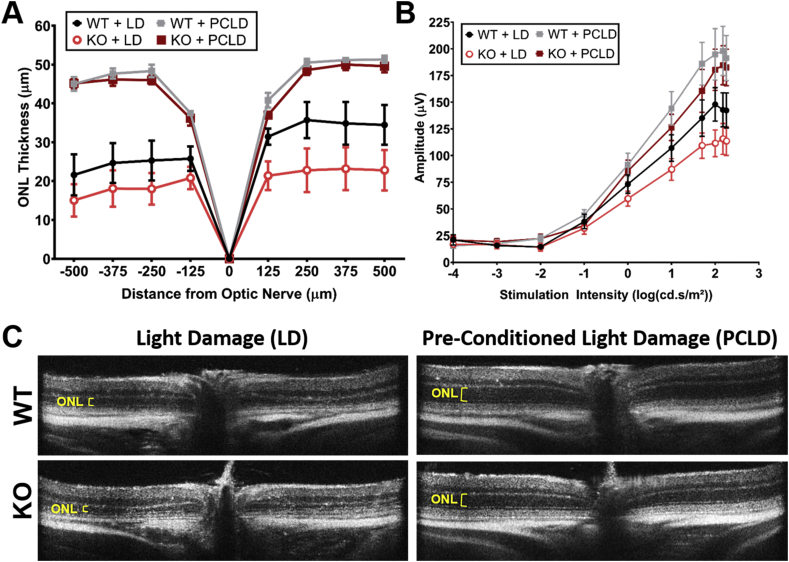
Fig. 4.
Knockout of PPARδ does not significantly increase sensitivity to light damage and PPARδ is not required for preconditioning-induced protection from light damage. (A) Quantification of the outer nuclear layer (ONL) thickness at 125 μm intervals from the optic nerve head to 500 μm in the inferior and superior directions from PPARδ WT and KO mice exposed to light damage (LD) or preconditioning and then light damage (PCLD). Two-way ANOVA, n = 11 for WT + LD, n = 10 for KO + LD, n = 3 for WT + PCLD, and n = 7 for KO + PCLD, plotted error represents standard error of the mean (SEM). There were no statistically significant differences between the KO and WT ONL thickness when exposed to LD (P ≥ 0.07) or PCLD (P ≥ 0.97). (B) Scotopic ERG a-wave amplitude, corresponding to photoreceptor function in PPARδ KO or WT mice with LD or PCLD. Two-way ANOVA, n = 5 per group, plotted error represents standard error of the mean (SEM). There were no statistically significant differences between the KO and WT a-wave amplitudes when exposed to LD (P ≥ 0.17) or PCLD (P ≥ 0.48). (C) Representative OCT images from WT or KO mice exposed to LD (left column) or PCLD (right column).