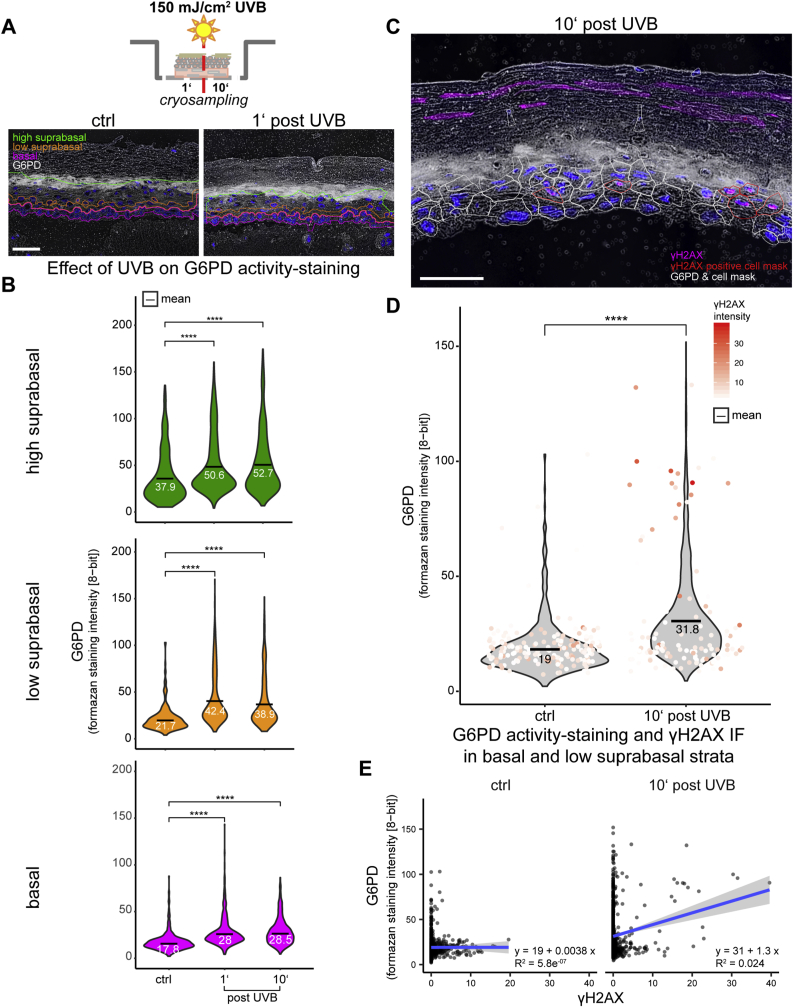
Fig. 3.
UVB exposure of human epidermal skin equivalent models leads to immediate increase of G6PD activity staining.
Fully stratified human epidermal skin equivalents were irradiated with UVB (150 mJ / cm²) and cryo-samples were collected one and 10 minutes after end of irradiation (A, top scheme). Shown are representative graphs from 3 independent experiments.
(A) Lower panels: Inverted brigh-tfield images of G6PD activity staining in cryosections from control skin equivalents and one minute post irradiation. Basal and low suprabasal strata indicated by pink and orange contour respectively. (B) Violin plots of G6PD activity staining at the indicated time points within the indicated strata. (C) Inverted bright-field image of cryosections from skin equivalents 10 minutes post irradiation with overlaid IF staining for γH2AX. White outlines indicate predicted cellular measurement masks, cell masks of γH2AX positive cells are marked by red contours. D) Violin plots of G6PD activity staining in the combined basal and low suprabasal strata of control samples and samples taken 10 minutes post irradiation to which values of γH2AX positive cells are superimposed, the color gradient indicating relative IF staining intensity. (E) Scatter plots of G6PD activity staining in the combined basal and low suprabasal strata of control samples and samples taken 10 minutes post irradiation versus γH2AX-staining intensity with regression lines (gray: 95% CI). For B and D the mean values are indicated by black bars with subscripted numeric values. Asterisks indicate statistical differences (****- p<0.0001; Student’s t-test calculated with R software). Size bars: 50µm.