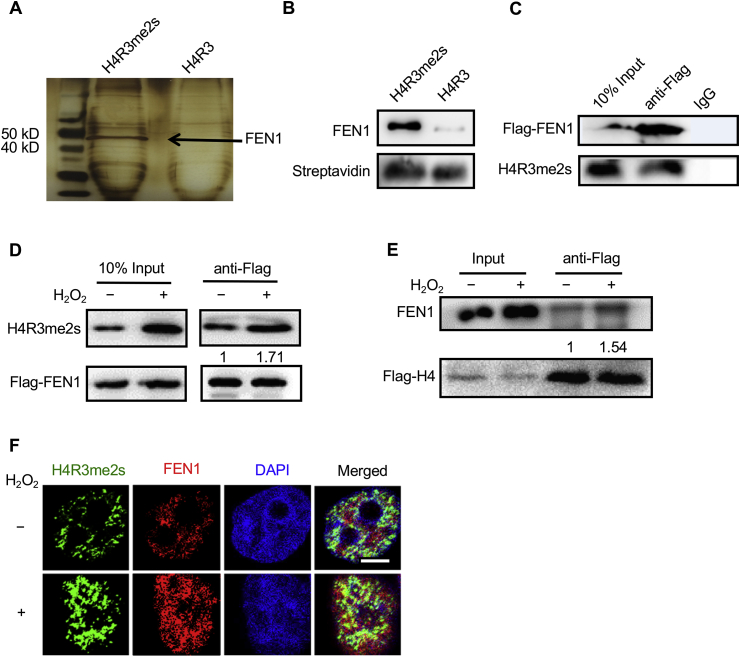
Fig. 4.
H4R3me2s interacts with FEN1 in vitro and in vivo. (A) Nuclear extracts of HeLa cells were subjected to pull down assays with biotin-labeled H4R3me2s or H4R3 peptides. The eluted protein complex was separated by SDS-PAGE and silver stained. The indicated gel slices were processed for protein identification using mass spectrometry. (B) Recombinant FEN1 was pulled down with biotinylated H4R3me2s or H4R3 N-terminal tail peptides. (C) Whole-cell extracts of HEK293T cells harboring Flag-FEN1 were subjected to co-IP assay with M2 Flag-tagged magnetic beads or control IgG, followed by IB with anti-H4R3me2s antibody. (D) HEK293T cells transfected with Flag-FEN1 were treated with or without 1 mM H2O2 for 30 min, and whole-cell extracts were then collected. A co-IP assay was performed with anti-Flag antibody M2 beads, followed by IB with anti-H4R3me2s antibody. (E) HEK293T cells transfected with Flag-H4 were treated with or without 1 mM H2O2 for 30 min, and whole-cell extracts were then collected. A co-IP assay was performed with anti-Flag M2 beads, followed by IB with anti-FEN1 antibody. The numbers in the figure represent the relative grey values of the bands above (regard control treatment group as 1, quantified with Image J software). (F) HeLa cells were treated with 1 mM H2O2 for 30 min, the medium was then changed to fresh medium. After 4 h, the cells were fixed and immunostained with antibodies against H4R3me2s (green) and FEN1 (red). DNA was stained with DAPI (blue), and cells were visualized by laser confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 10 μm. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)