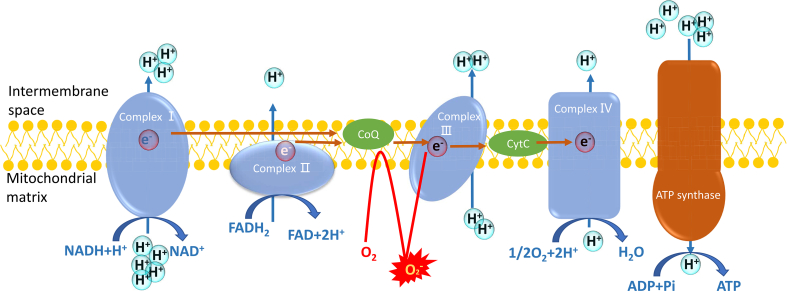
Fig. 1.
The electron transportation chain and the generation of ROS in mitochondria. Complex I and II receive the electrons from NADH and FADH2, respectively. Then the electrons are transported to coenzyme Q (CoQ), and then transferred to cytochrome C (Cyt C) in the complex III. Finally, complex IV offers the electrons to O2 to produce H2O. In this process, all the complexes pump protons out of mitochondrial matrix to form a gradient of protons between intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix. The energy of the proton gradient drives ATP synthase to generate ATP. Hyperglycemia can induce the blockage of the normal electron transportation, and O2 can accept the electrons to transform into reactive oxygen species.