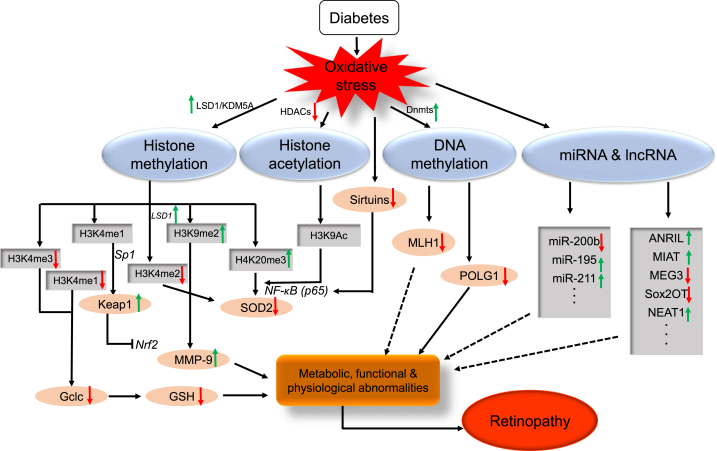
Fig. 4.
Schematic diagram of epigenetic modifications in DR: diabetes induces oxidative stress, which leads to the altered expression of genes involved in histone (LSD1, KDM5A, HDACs), and DNA (DNMTs) modifications. Histone methylation (H3K4me1, H3K4me3H3K9me2, H3K4me2, H4K20me3) and acetylation (H3K9-Ac, p65 of NF-κB) modulate the binding of transcription factor (Nrf2, Sp1, NF-kB-p65) and alter the transcriptional levels of Gclc, Keap1, MMP-9, SOD2, and TXNIP. DNA methylation at POLG1 and MLH1 promoter represses their transcriptional levels in DR. MicroRNAs (miR-200b, miR-195, miR-211 …) and lncRNA (ANRIL, MIAT, MEG3, Sox2OT, NEAT1 …) regulate their target genes related to the development of DR. Although this scheme shows various epigenetic regulation, we cannot exclude the roles of many, yet identified, other histone and DNA modifications and miRNAs and lncRNA in DR.