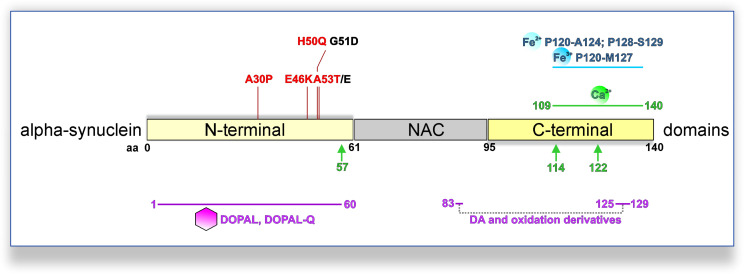
FIGURE 1.
PD-linked SNCA mutations and interactions with DA metabolites, calcium, or iron promoting pathological aSyn oligomerization and/or aggregation. PD-linked SNCA missense mutations that increase the oligomerization and/or fibrillization of aSyn in vitro are shown in red (otherwise black). DA and oxidation derivatives bind non-specifically to the C-terminus (aa 125–129), further stabilized by long-range electrostatic interactions with E83 of the NAC region (intermittent gray line). Also, DOPAL/DOPAL-Q adducts with N-terminal aSyn lysines are formed at the 1–60 domains (purple line). Fe2+ (ferrous) and Fe3+ (ferric) iron bind to adjacent regions at the C-terminus of aSyn (blue line; Fe2+: aa P120-A124 and P128-S129; Fe3+: aa P120-M127). Moreover, a calcium-binding motif has been mapped to the C-terminus of aSyn (green line; aa 109–140). Calcium also promotes calpain I-mediated cleavage of aSyn, with three major cleavage sites depicted (green arrows; monomeric aSyn: after aa 57; fibrillar aSyn: after aa 114 and 122).