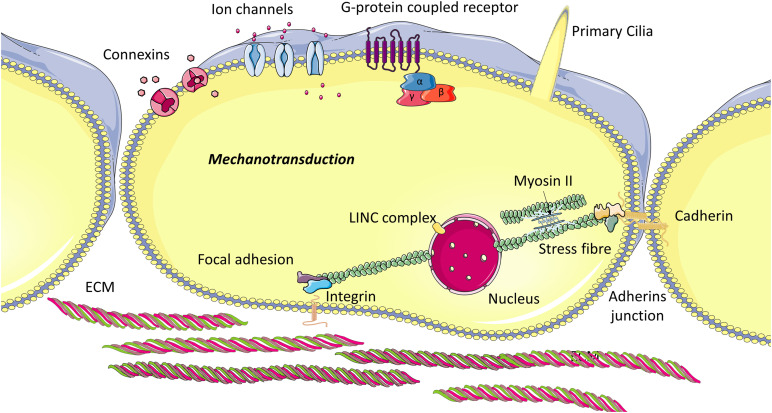
FIGURE 2.
Cellular mechanosensory proteins: The internal cytoskeleton transmits mechanical stimuli from the extracellular environment to the cell nucleus. This stimulus is mediated by transmembrane proteins located at focal adhesions, which bind to ECM ligands but also intracellular proteins. Cadherins connect the cytoskeleton of adjacent cells and thus enable cells to transmit force from one to another, and also allow movement of components within the plasma membrane. Primary cilia sense fluid flow, pressure and strain and activate ion flux through channels on the ciliary axoneme, which govern intracellular signaling. Other membrane proteins can also be regulated through mechanical shear and strain.