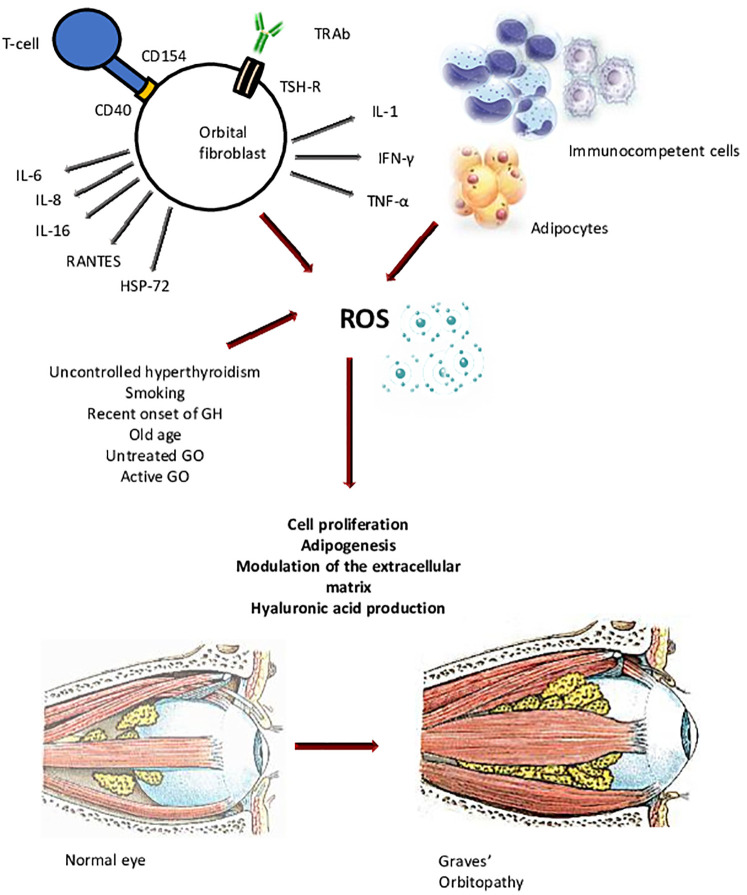
Figure 1.
Orbital fibroblasts (OFs) are activated by both cellular and humoral immune responses against autoantigens, among which the thyrotropic hormone (TSH) receptor (TSH-R) is the main involved. The inflammatory process triggers the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, growth factors, chemokines, and ROS, which contribute the increased proliferation of OFs, the differentiation of connective orbital cells into pre-adipocytes and then adipocytes, and the synthesis of great amounts of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), especially hyaluronic acid. The resulting orbital remodeling is characterized by extraocular muscle enlargement and orbital fat expansion, which are ultimately responsible for the clinical manifestations of the disease. IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-8, interleukin-8; IL-16, interleukin-16; RANTES, regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed and presumably secreted; HSP-72, heat shock protein-72; IL-1, interleukin-1; IFN-γ, interferon γ; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; GH, Graves’ hyperthyroidism; GO, Graves’ orbitopathy.