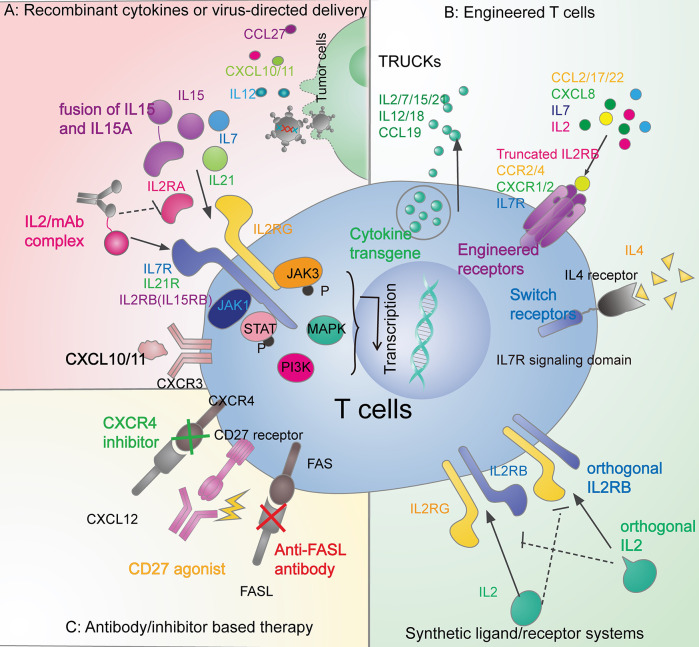
Figure 2.
Therapeutic strategies in overcoming the T-cell exclusion by leveraging the cytokine signals. (A) Recombinant cytokines or virus-directed delivery. Administration of recombinant IL2 (94), IL7 (95), and IL15 (96, 97) have brought success in clinical trials. Also, there are other recombinant cytokines under research in preclinical models, such as IL21 (98), and CXCL10 (24). Adenoviral, retrovirus, and vaccinia vectors can also deliver cytokines, including CCL27 (41), IL12 (99, 100), CXCL10 (26), and CXCL11 (25). (B) Engineered T cells. The fourth-generation CAR T cells (TRUCKs) can release IL2 family cytokines (IL2, IL7, IL15, and IL21) (101), IL12, IL18 (102) and CCL19 (103). CAR T cells can also be engineered with functional receptors such as CCR2 (30, 31), CCR4 (66), CXCR1/2 (54), IL7R (54, 104), truncated IL2B domain (105), and switch receptors to overcome the immune-suppressive cytokines (106). Tumor-specific T cells can also be equipped with synthetic ligand/receptor systems such as IL2 and IL2RB orthogonal pairs (107). (C) Antibody/inhibitor-based therapy. Agonistic (105, 108) or antagonistic (109) antibodies and inhibitors (58) are applied to modulate cytokine signaling pathways in the anticancer immune response.