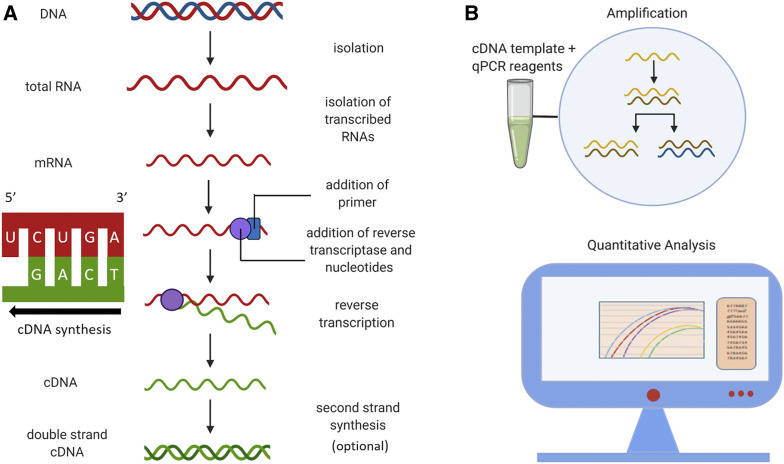
Figure 4.
Workflow for cDNA isolation and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). (A) Total RNA is isolated from samples and is reverse transcribed in a 5′ to 3′ direction to form complementary DNA (cDNA). This step requires a reverse transcriptase (RT) enzyme which uses mRNA as a template. Depending on the type of RT used and whether RNase is added to the RT reaction, the initial product is either a single-stranded cDNA or a DNA::RNA hybrid. Second strand synthesis is an optional step to produce double-stranded cDNA which may be useful for other applications, such as molecular cloning or generating cDNA libraries. (B) The cDNA and qRT-PCR reagents are added to a microwell plate (a single tube is shown for simplicity). Negative controls (not shown) include the following: (1) a no-template control, (2) a no-reverse-transcriptase control, and (3) a no-amplification control, meaning no DNA polymerase. During qRT-PCR, amplification and quantification of cDNA occur simultaneously. Experimental and positive control reactions are depicted by colored curves on data analysis display, and horizontal black line corresponds to negative control.