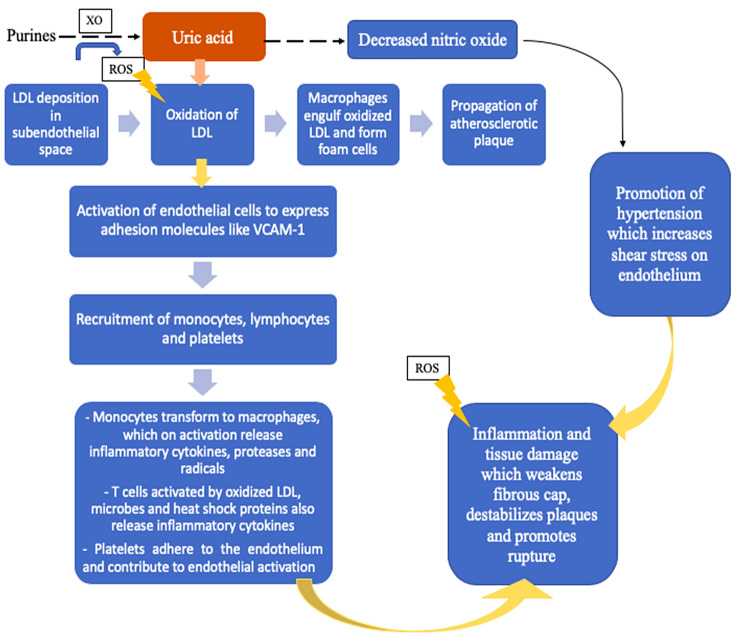
Fig. 2.
A simplified representation of the role of uric acid in atherogenesis and cardiovascular disease. Other proposed mechanisms, not represented here, are activation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system and insulin resistance. LDL low-density lipoprotein, ROS reactive oxygen species, VCAM-1 vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, XO xanthine oxidase