Figure 5.
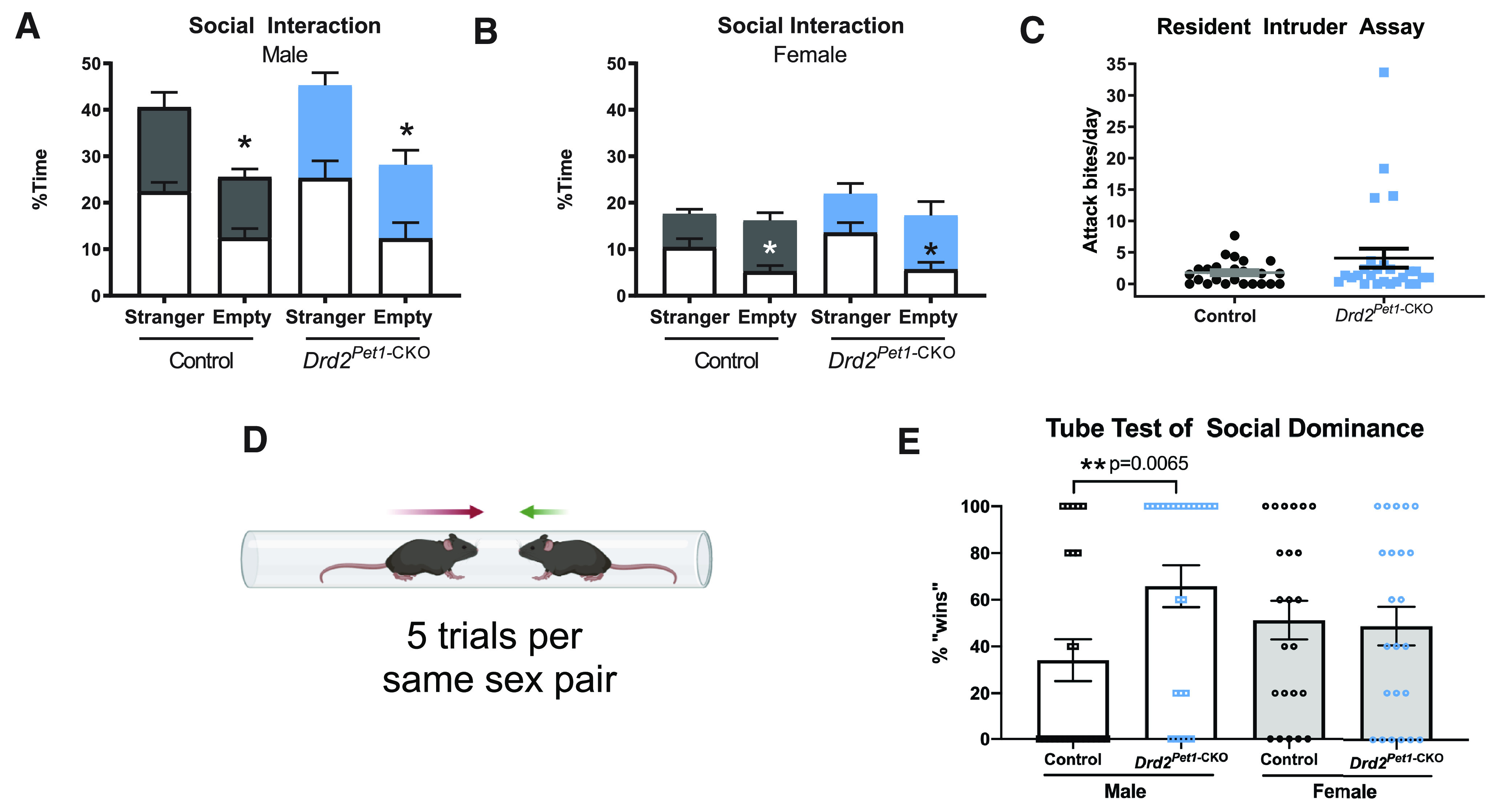
Drd2Pet1-CKO males, but not females, display increased social dominance. A, B, Three chambered social interaction assay. No significant difference in time spent investigating a stranger mouse or an empty holder for (A) males (n = 8 controls compared with 6 Drd2Pet1-CKO, p = 0.541, unpaired t test) and (B) females (n = 7 controls compared with n = 5 Drd2Pet1-CKO, p = 0.358, unpaired t test). Investigation time is binned into 5-min intervals where white bars indicate first 5 min of assay and colored bars indicate last 5 min of assay. As expected, mice of both genotypes spent significantly less time investigating the empty holder than the stranger mouse noting that females of both genotypes only did so during the first 5 min of the assay. C, Resident intruder assay of aggression. No significant difference in the average attack bites per day delivered to a Swiss Webster intruder mouse was observed between Drd2Pet1-CKO males (n = 26, 4.07 ± 1.50 bites) aggression levels were not significantly different from controls (n = 24, 1.77 ± 0.39 bites; Mann–Whitney, two-tailed, U = 289.5, p = 0.6649). D, Schematic of tube test (for details of assay, see Materials and Methods). Schematic created with BioRender. E, Drd2Pet1-CKO males (n = 24) demonstrate more dominance behavior than controls (n = 24) as they displayed increased winning in the tube test (controls: 34.17 ± 9% wins, Drd2Pet1-CKO: 65.83 ± 9% wins, p = 0.0065, Mann–Whitney, two-tailed, U = 166). Female Drd2Pet1-CKO (n = 23) showed no difference in social dominance compared with controls (n = 23; controls: 51.3 ± 8%, Drd2Pet1-CKO: 48.7 ± 8% wins, p = 0.8123 Mann–Whitney, two-tailed, U = 253).
