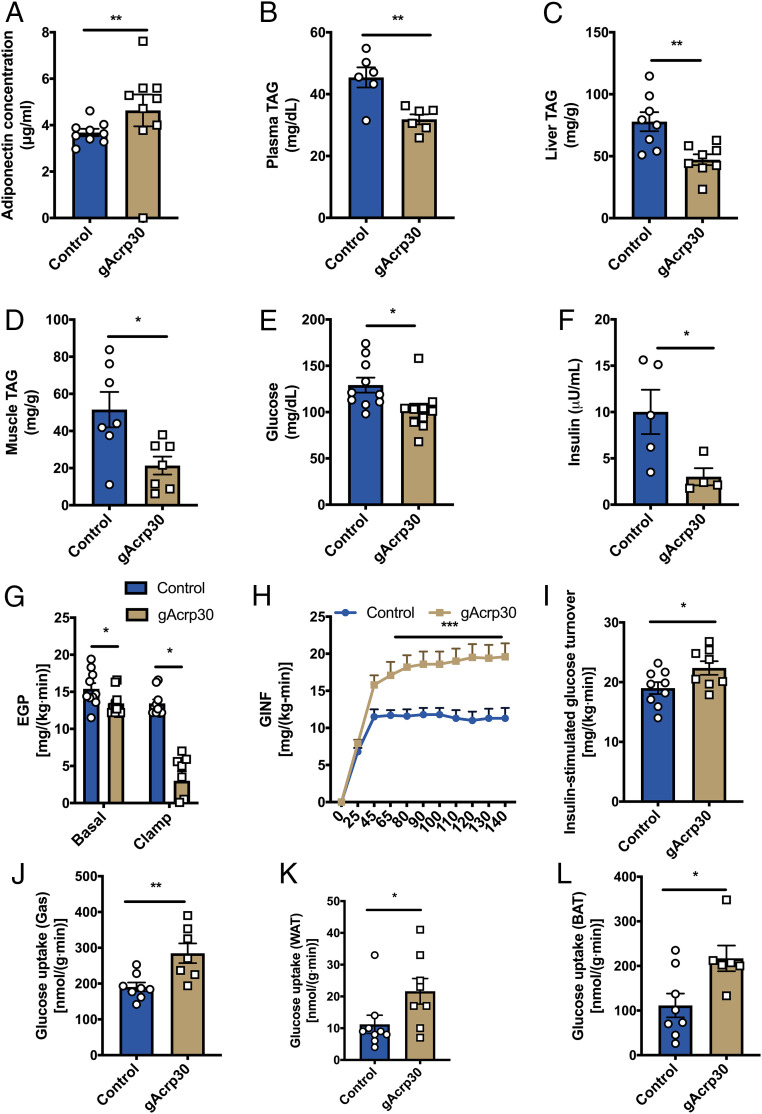
Fig. 1.
Globular adiponectin treatment ameliorates lipid-induced insulin resistance in HFD-fed mice. (A) Plasma adiponectin concentrations after overnight fasting in HFD-fed mice treated with globular adiponectin (gAcrp30) or vehicle-control for 2 wk. (B) Plasma TAG concentrations of control and gAcrp30-treated mice after overnight fasting. (C and D) Liver and muscle TAG content of control and gAcrp30-treated mice. (E and F) Plasma glucose (n = 10) and insulin concentrations (n = 4–5) of control and gAcrp30-treated mice after overnight fasting. (G) Endogenous glucose production rate under basal and the hyperinsulinemia-euglycemia clamp states (n = 8–10). (H) Glucose infusion rate during the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp. (I) Glucose turnover rate during the hyperinsulinemia-euglycemia clamp. (J–L) Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake rate in skeletal muscle, WAT, and brown adipose tissue in control and gAcrp30-treated mice. Data are shown as mean ± SEM *P < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparisons for G. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by unpaired Student’s t test for other graphs.