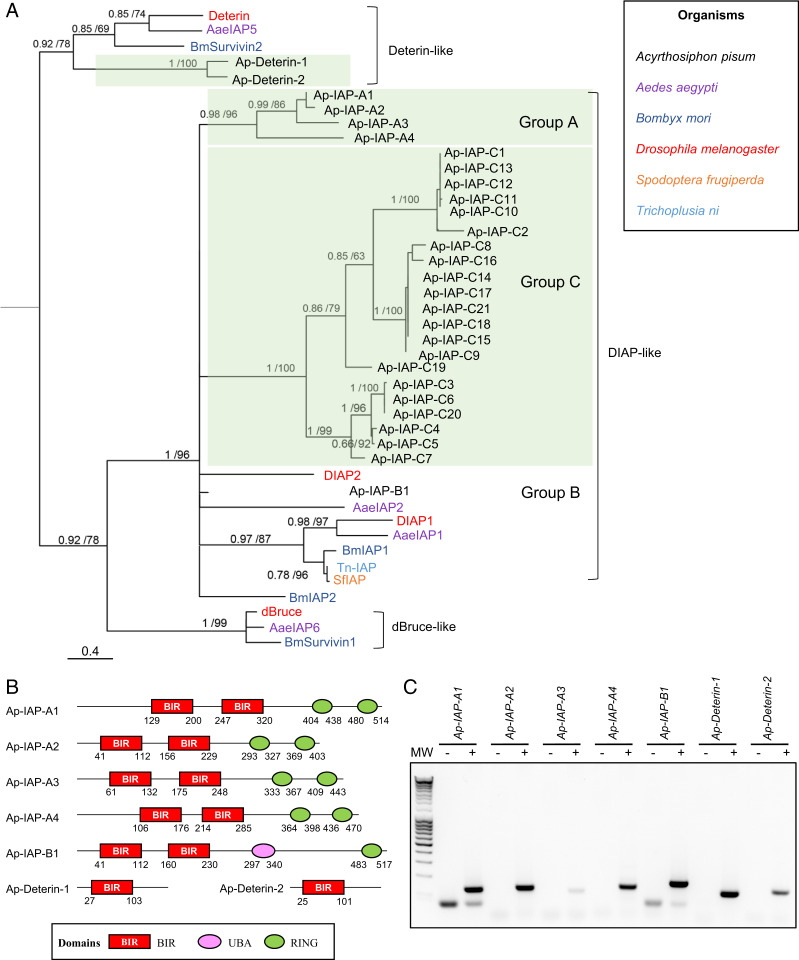
Fig. 2.
Identification of IAP-encoding genes in the pea aphid genome. (A) The phylogenetic relationships between IAP protein sequences found in Acyrthosiphon pisum and a selection of insect species based on BIR domain alignment. For each node, Bayesian posterior probability and bootstrap values are indicated. A group of putative A. pisum IAP paralogs are also indicated. This tree was generated using one representative BIR domain from each IAP sequence (full procedure described in the SI Appendix, Supplementary Materials and Methods). Midpoint rooting was used to present the tree. (B) The domain architecture of selected pea aphid putative IAPs. Each IAP contains at least one BIR domain (Baculoviral IAP Repeat). Additional domains include UBA (ubiquitin-associated domain) and/or RING domains. The positions of amino acids that mark the beginning and the end of the different domains are indicated below each structure. (C) Pea aphid putative IAP genes are expressed. The sequences were successfully amplified from a pool of cDNA obtained from whole aphids at different life stages. For each primer set, a negative control was performed on samples devoid of cDNA. MW, molecular weight marker.