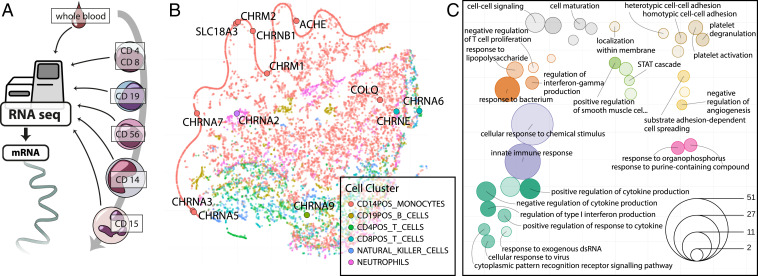
Fig. 4.
Immune cell gene-expression clustering and long RNA pathways perturbed in stroke blood. (A) Published cell type-specific long RNA profiles (25) were used to visualize transcriptomes of T lymphocytes (CD4+ T helper cells and CD8+ T cytotoxic cells), B lymphocytes (CD19+), NK cells (CD56+), monocytes (CD14+), and neutrophils (CD15+). (B) t-SNE visualization of 15,032 genes on the basis of their expression in blood-borne immune cells extrapolated from transcriptional activities in regulatory circuits (25). Genes are colored by the cell type in which their expression was highest. Cholinergic core and receptor genes were mainly found in the CD14+ monocytic compartment. (C) Enrichment of poststroke DE genes (log2FC > 1.4) in circulation- and immunity-related pathways, presented as t-SNE of GO terms by their shared genes (SI Appendix, Expanded Methods); color denotes t-SNE cluster, size denotes number of significant genes in term; deeper color indicates lower enrichment P value (all P < 0.05). Distance between terms indicates the number of shared genes between the GO terms, closer meaning more shared genes.