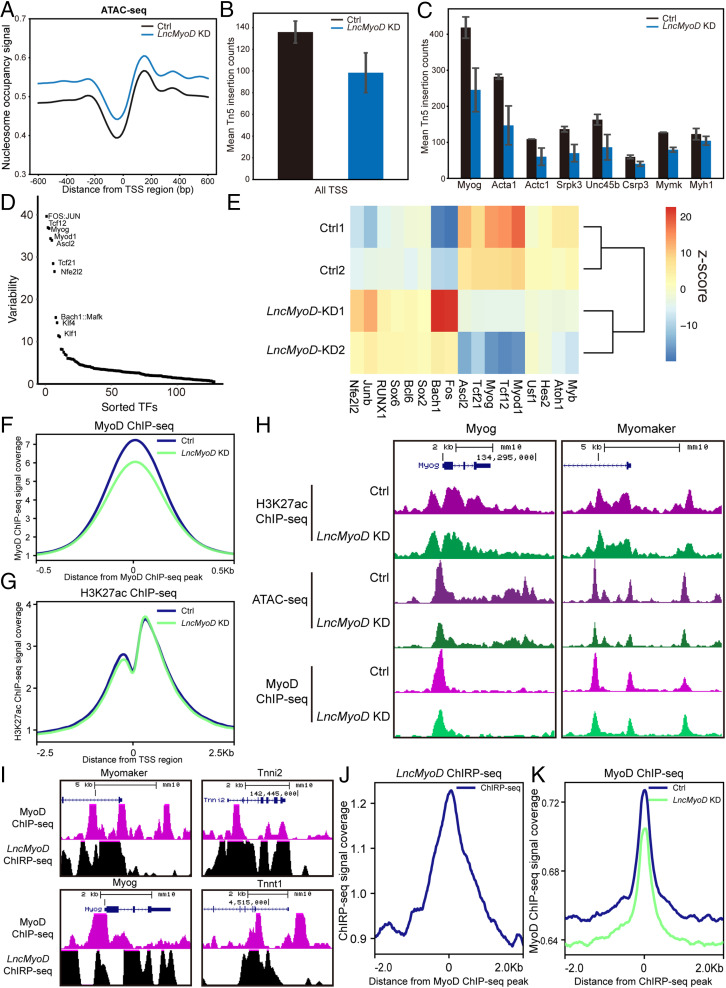
Fig. 6.
LncMyoD functions as a chromatin modifier to promote the transcription of myogenesis-related genes. (A) Distribution of nucleosome occupancy signal across all TSS regions (B and C) Calculation of Tn5 insertion counts of all TSS regions (B) and TSS regions of typical myogenesis-related genes (C). (D) chromVAR analysis of different TF motif accessibility changes between the Ctrl and LncMyoD KD groups. Graph represents the ranking of the variability of TF motifs accessibility changes. (E) Heat map showing Z score of TF motif accessibility changes between the Ctrl and LncMyoD KD groups. (F) Distribution of MyoD ChIP-seq signal across all MyoD binding sites. (G) Distribution of H3K27ac ChIP-seq signal across all MyoD binding sites. (H) Genome tracks of the Myog and Myomaker loci showing ATAC-seq, H3K27ac ChIP-seq, and MyoD ChIP-seq across their promoter regions in the Ctrl and LncMyoD KD groups. (I) Genome tracks of the Myog, Myomaker, Tnni2, and Tnnt1 loci showing LncMyoD ChIRP-seq and MyoD ChIP-seq across their promoter regions. (J) Distribution of LncMyoD ChIRP-seq signal across all MyoD binding sites. (K) Distribution of MyoD ChIP-seq signal across all LncMyoD binding sites.