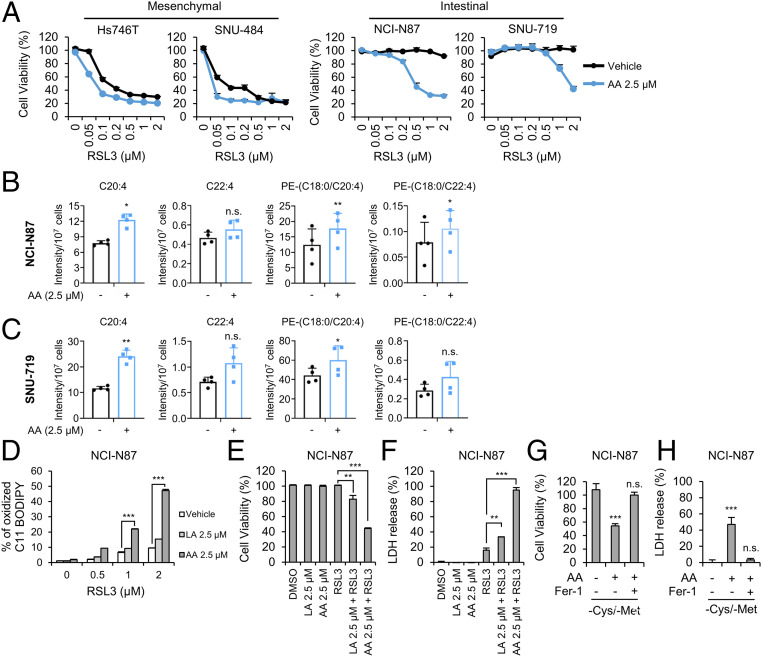
Fig. 5.
Exogenous AA supplementation restores the sensitivity of intestinal-type GCs to ferroptosis. (A) Relative viability of GCs pretreated with 2.5 μM of AA for 16 h and treated with RSL3 for 24 h. Data are the means ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). (B and C) Levels of the indicated lipids in NCI-N87 and SNU-719 cells treated with 2.5 μM AA for 3 h determined using LC-MS/MS. Intensities were normalized to cell numbers. Data are the means ± SD (n = 4 independent experiments), with *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01 according to two-sided Student’s tests (n.s. denotes not significant). (D) Lipid peroxidation levels in NCI-N87 cells pretreated with 2.5 μM PUFAs for 16 h and treated with RSL3 for 1 h. Data are the means ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments), with ***P < 0.001 according to two-sided Student’s tests. (E and F) Cell viability and cell death as measured by LDH release from NCI-N87 cells pretreated with LA and AA for 16 h and treated with RSL3 for 24 h. Data are the means ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments), with **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 according to two-sided Student’s tests. (G and H) Cell viability of and LDH release from NCI-N87 cells cultured with cysteine/methionine-deficient medium in the presence and absence of AA and Fer-1. Data are the means ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments, n.s. denotes not significant, ***P < 0.001 according to two-sided Student’s t tests).