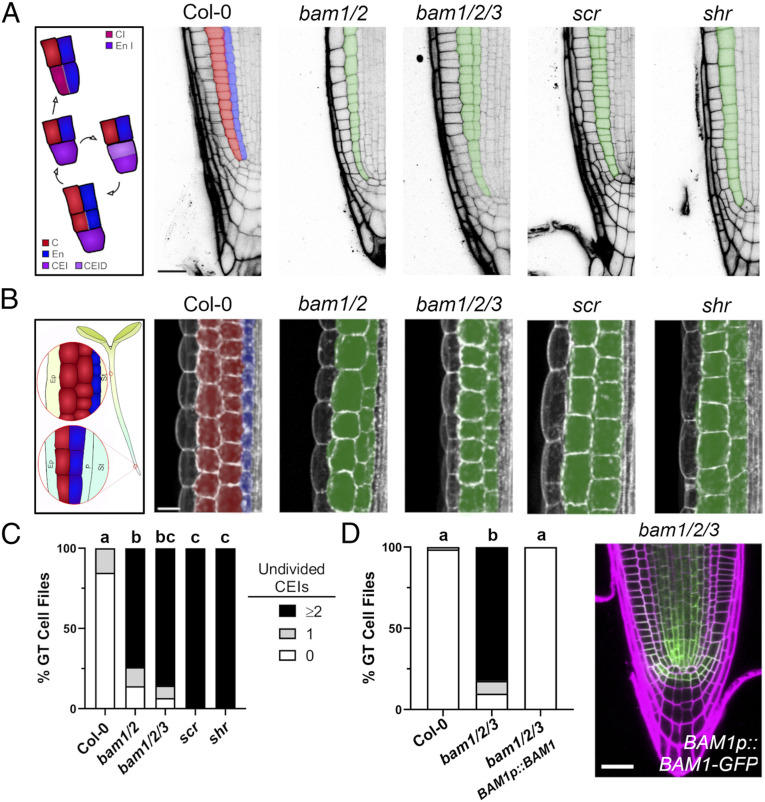
Fig. 1.
BAM1/2 receptor kinases are required for formative ground tissue divisions. Confocal images of scr, shr, and higher order bam mutants at 7 dag with similar defects in ground tissues in root (A) and hypocotyl tissues (B). Cortex (red), endodermis (blue), mutant ground tissue layers (green). (C) Undivided CEIs (0, 1, or ≥2) were quantified in each ground tissue (GT) cell file in each mutant (n = 88, Col-0; n = 54, bam1/2; n = 59, bam1/2/3; n = 139, scr; and n = 108, shr). (D) BAM1p::BAM1-GFP rescues CEI divisions in bam1/2/3 mutant roots (n = 68, Col-0; n = 70, bam1/2/3; and n = 102, bam1/2/3 BAM1p::BAM1-GFP). Distributions were compared using a Kruskal–Wallis nonparametric test. C, cortex; En, endodermis; CEI/CEID, cortex/endodermal initial/daughter; CI, cortex initial; En I, endodermal initial; Ep, epidermis; P, pericycle; St, stele.