Figure 11.
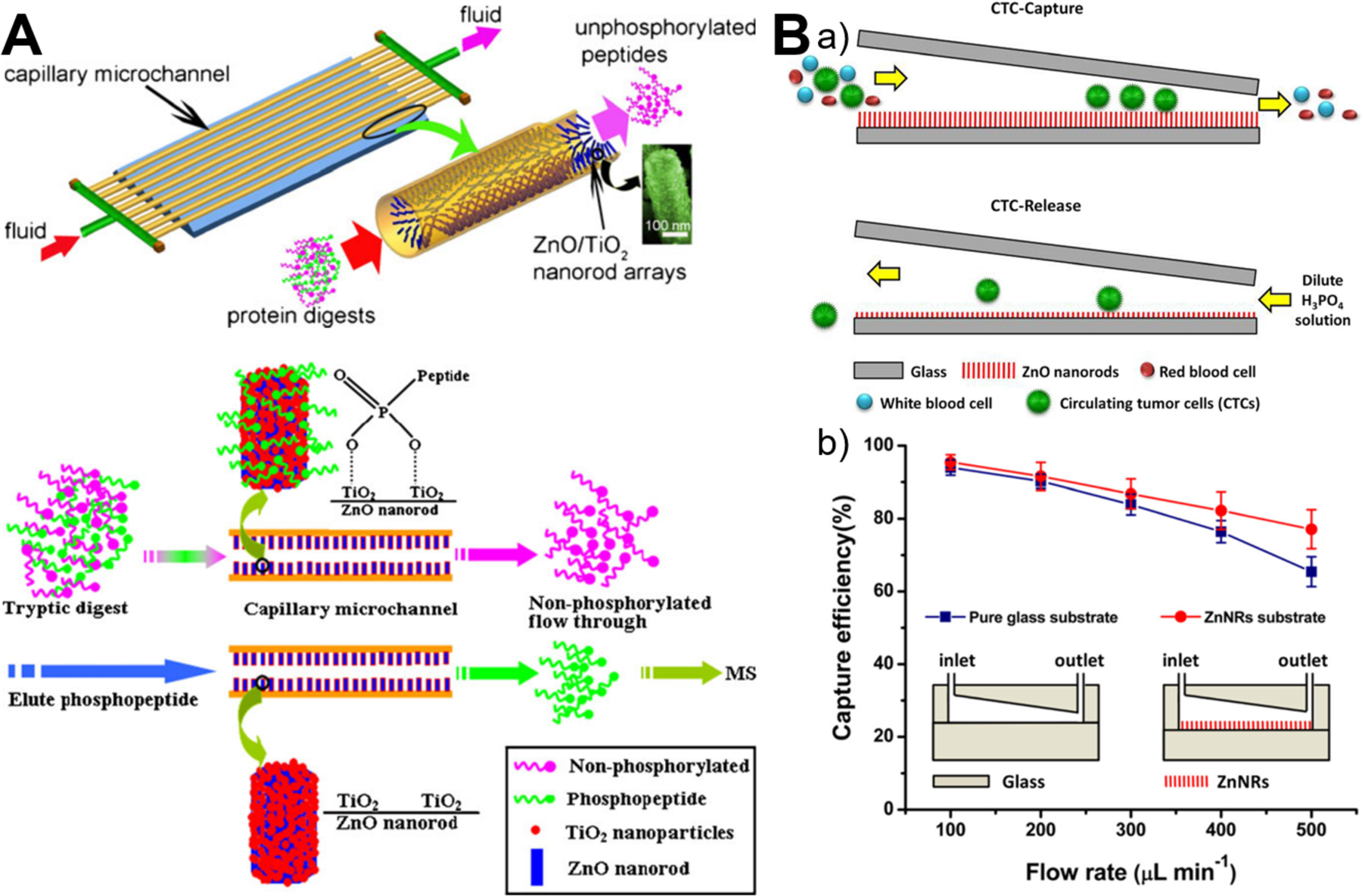
Microfluidics-enabled biological separation applications of ZnO materials. (A) Continuous high-throughput phosphopeptide enrichment using microfluidic channels modified with aligned ZnO/TiO2 nanorod arrays. Reproduced with permissions from reference84, copyright 2011, Springer Nature. (B) Highly efficient isolation and release of circulating tumor cells based on size-dependent filtration and degradable ZnO nanorods substrate in a wedge-shaped microfluidic chip (a), and capture efficiency of spiked SKBR3 cells at different flow rates in two kinds of microfluidic chips with/without ZnO nanorods substrate (b). Reproduced with permissions from reference95, copyright 2017, Springer Nature.
