Extended Data Figure 8. RNA in situ hybridization and histopathological analysis of VEEV infection in Ldlrad3-D1-Fc or isotype control treated mice.
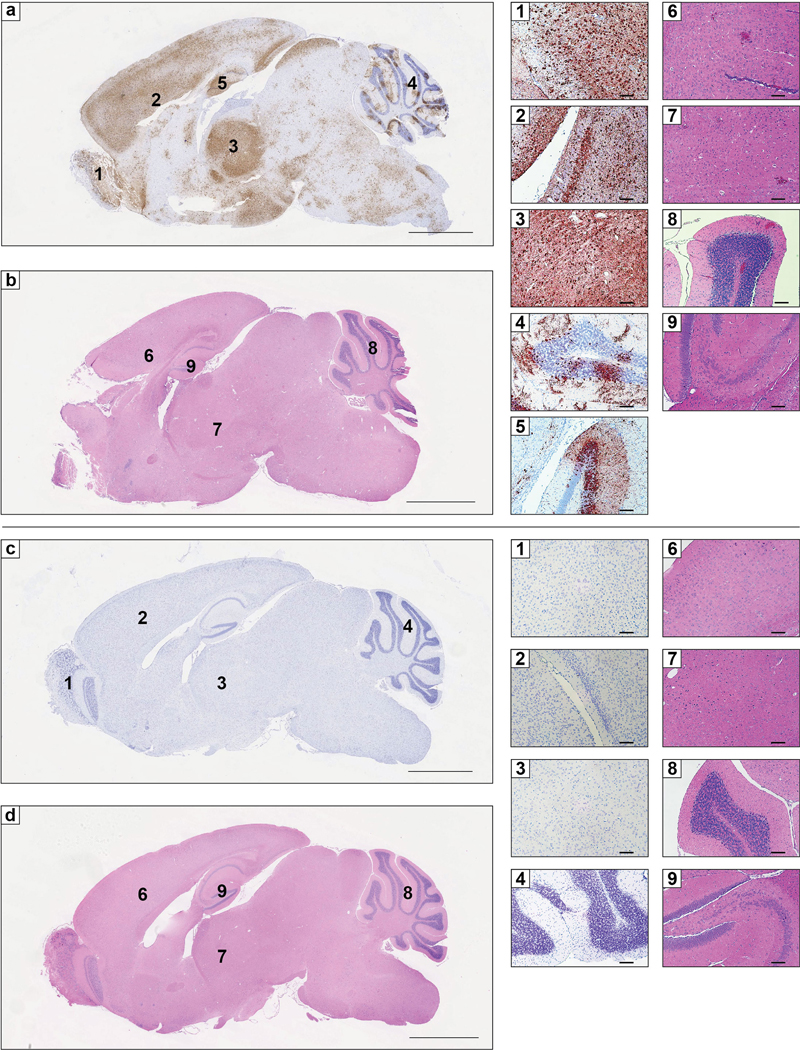
a-d. Six-week-old C57BL/6J mice were administered 250 μg of isotype control mAb JEV-13 (a-b) or Ldlrad3-D1-Fc (c-d) via intraperitoneal route 6 h prior to subcutaneous inoculation of 102 FFU of VEEV ZPC738. Six days post-infection, brain tissues were harvested, fixed, paraffin-embedded, and subjected to RNA in situ hybridization using VEEV ZPC738-specific probes (a and c) and hematoxylin and eosin staining (b and d). Scale bars, 2 mm. Representative high-power (10X) magnification insets of the olfactory bulb (1), cortex and midbrain (2), thalamus (3), cerebellum (4), and hippocampus (5) are shown for isotype control (a, top) or Ldlrad3-D1-Fc (c, bottom) treated mice. Scale bars, 100 μm. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of brain sections from isotype control (b) or Ldlrad3-D1-Fc (d) treated mice. Scale bars, 2 mm. Representative high-power (10X) magnification insets of the cerebral cortex (6), thalamus (7), cerebellum (8), and hippocampus (9) are shown for isotype control (b, top) or Ldlrad3-D1-Fc (d, bottom) treated mice. Scale bars, 100 μm. Representative images from one experiment (n = 5 per group) are shown.
