Figure 9.
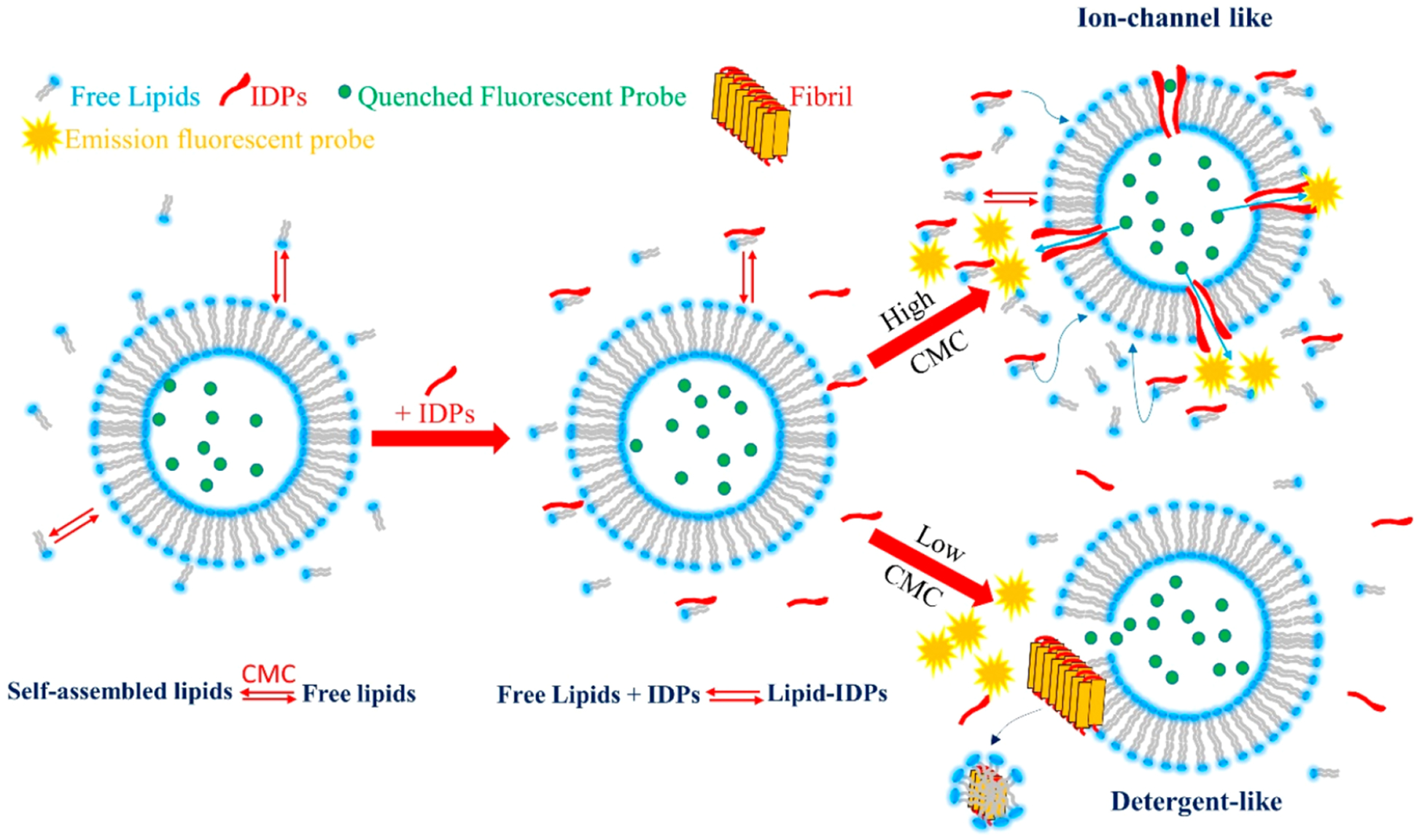
Schematic drawing illustrating how IDPs interact with a model membrane in the presence of free lipids at different CMC values in the aqueous phase. Self-assembled lipids are in chemical equilibrium with free lipids in the aqueous phase (free lipids). There is a continuous exchange between self-assembled and free lipids. The concentration of free lipids remains constant over time (CMC). By the addition of IDPs, a stable lipid–IDP complex is formed in the water phase. Two pathways can occur depending on the CMC values. A high CMC value favors ion-channel-like pores, whereas a low CMC favors detergent-like mechanism. At intermediate CMC values, both mechanisms are feasible. In the presence of nonamyloidogenic proteins, lipid–protein complex formation is not favored, thus no protein insertion into bilayer occur.
