FIGURE 3.
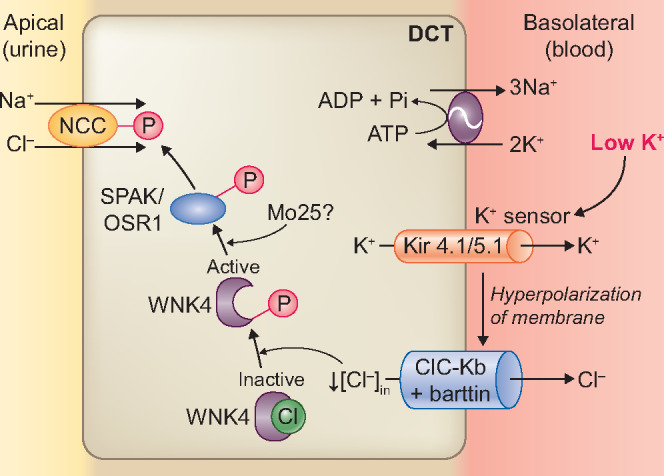
Molecular pathways involved in the effects of a low K+ diet on the NCC. A low extracellular K+ concentration is sensed by the K+ channel Kir 4.1/5.1, resulting in efflux of K+ through Kir4.1/5.1. This leads to membrane hyperpolarization and chloride (Cl−) efflux through a basolateral voltage-gated Cl−channel (ClC-Kb/barttin). A reduction in intracellular Cl− concentration relieves the inhibition of WNK4 autophosphorylation. In turn, phosphorylated WNK4 activates SPAK–OSR1, which phosphorylates NCC. In Drosophila melanogaster kidney tubules, WNK4 phosphorylation of SPAK–OSR1 depends on the scaffold protein Mo25.
